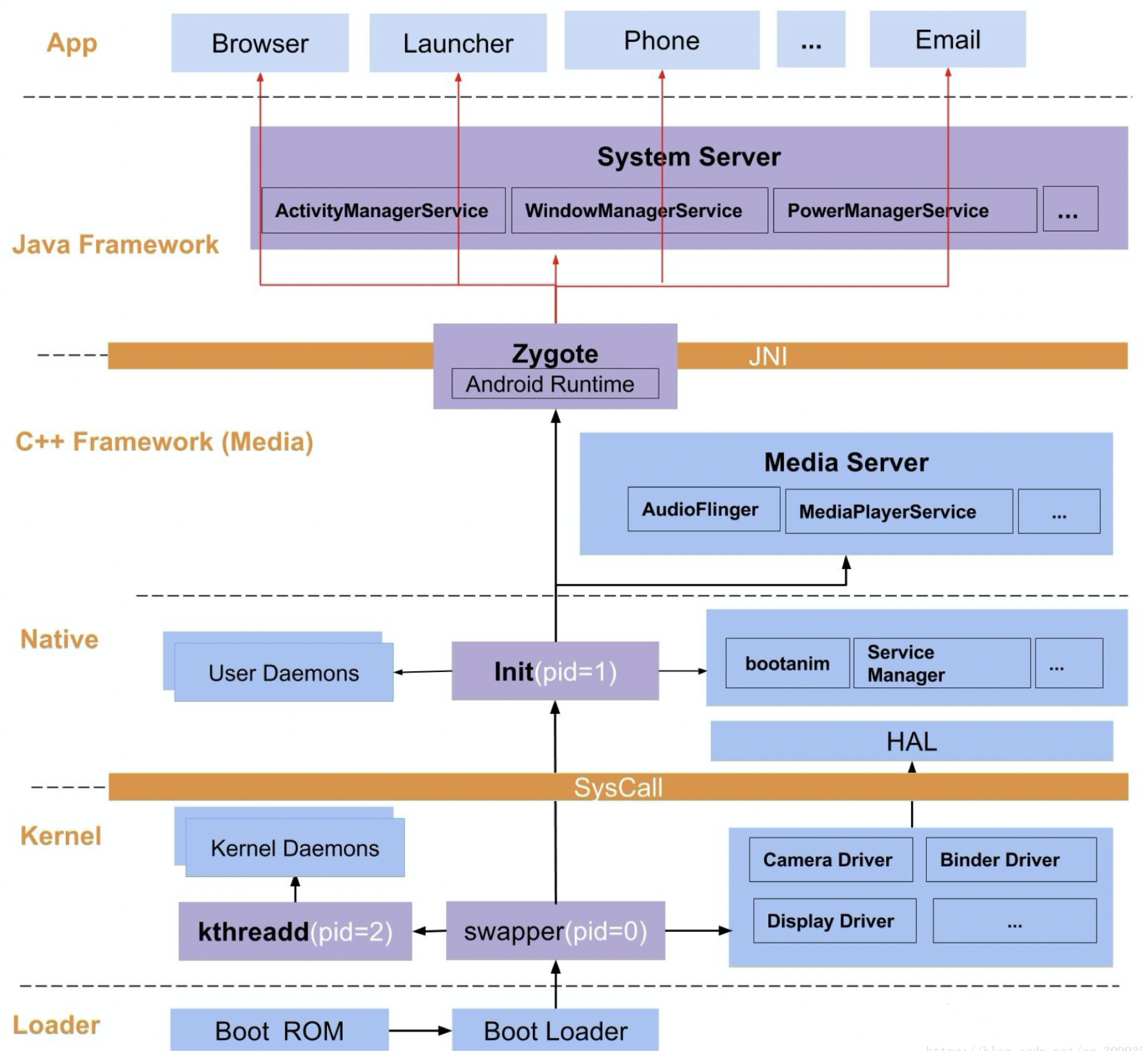
1. 启动流程 Android系统启动过程往细了说可以分为5步:
Loader –> Kernel –> Native –> Framework –> Application
1.1 Loader
1.2 Kernel Kernel层是指Android内核层,到这里才刚刚开始进入Android系统
启动Kernel的swapper进程(pid=0):该进程又称为idle进程, 系统初始化过程Kernel由无到有开创的第一个进程, 用于初始化进程管理、内存管理,加载Display,Camera Driver,Binder Driver等相关工作
启动kthreadd进程(pid=2):是Linux系统的内核进程,会创建内核工作线程kworkder,软中断线程ksoftirqd,thermal等内核守护进程。kthreadd进程是所有内核进程的鼻祖
1.3 Native 这里的Native层主要包括init孵化来的用户空间的守护进程、HAL层以及开机动画等。启动init进程(pid=1),是Linux系统的用户进程,init进程是所有用户进程的鼻祖
init进程会孵化出ueventd、logd、healthd、installd、adbd、lmkd等用户守护进程
init进程还启动servicemanager(binder服务管家)、bootanim(开机动画)等重要服务
init进程孵化出Zygote进程,Zygote进程是Android系统的第一个Java进程(即虚拟机进程),Zygote是所有Java进程的父进程
1.4 Framework
Zygote进程启动后,加载ZygoteInit类,注册Zygote Socket服务端套接字;加载虚拟机;加载类,加载系统资源
System Server进程,是由Zygote进程fork而来,System Server是Zygote孵化的第一个进程,System Server负责启动和管理整个Java framework,包含ActivityManager,PowerManager等服务
Media Server进程,是由init进程fork而来,负责启动和管理整个C++ framework,包含AudioFlinger,Camera Service等服务
1.5 Application
Zygote进程孵化出的第一个App进程是Launcher,即手机桌面APP,没错,手机桌面就是跟我们平时使用的APP一样,它也是一个应用
所有APP进程都是由zygote进程fork出来的
这些层之间,有的并不能直接交流,比如Native与Kernel之间要经过系统调用才能访问,Java层和Native层需要通过JNI进行调用
严格来说,Android系统实际上是运行于Linux内核上的一系列服务进程,这些进程是维持设备正常运行的关键,而这些进程的老祖宗就是init进程
2. 启动流程(以Zygote启动流程为例) 当内核启动完成后,就会创建用户空间的第一个进程,即init进程;后面所有的进程,比如Binder机制中的ServiceManager,Zygote都是由init进程孵化出来的
对比老版本差异 在Android Q中,对该机制做了一些改变
单一的init.rc,被拆分,服务根据其二进制文件的位置(/system,/vendor,/odm)定义到对应分区的etc/init目录中,每个服务一个rc文件。与该服务相关的触发器、操作等也定义在同一rc文件中。
1 2 3 /system/ etc/init,包含系统核心服务的定义,如SurfaceFlinger、MediaServer、Logcatd等。/vendor/ etc/init, SOC厂商针对SOC核心功能定义的一些服务。比如高通、MTK某一款SOC的相关的服务。/odm/ etc/init,OEM/ ODM厂商如小米、华为、OPP其产品所使用的外设以及差异化功能相关的服务。
下图为Android Q 中定义的所有服务
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 ./recovery/ root/init.rc/recovery/ root/ueventd.rc/recovery/ root/init.recovery.mt6762.rc/recovery/ root/init.recovery.mt6765.rc/vendor/u eventd.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.wmt_drv.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.volte_imsm_93.rc/vendor/ etc/init/m tk_agpsd_p.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ bootperf.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ audiocmdservice_atci.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.graphics.composer@2.1 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.gpu@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.volte_stack.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit_connectivity.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.fmradio_drv.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ netdagent.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ atcid_eng.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.vtservice_hidl.rc/vendor/ etc/init/m tkrild.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.health@2.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.wfca.rc/vendor/ etc/init/m odemdbfilter_service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.bt_drv.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.gps_drv.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ aee_aedv64.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.secure_element@1.0 -service-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.drm@1.2 -service.clearkey.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.log@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.thermal_manager.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.bip.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.cccimdinit.rc/vendor/ etc/init/m d_monitor.rc/vendor/ etc/init/mu xreport.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.drm@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.wlan_drv.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.drm@1.2 -service.widevine.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ wlan_assistant.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ camerahalserver.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ atci_service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.cas@1.1 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i psec_mon.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.thermal@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.gatekeeper@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.keymaster@4.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.thermalloadalgod.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.graphics.allocator@2.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.mtkpower@1.0 -init.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ lbs_hidl_service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.sensors@2.0 -service-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hostapd.android.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.thermal.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ fuelgauged_nvram_init.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ em_hidl_eng.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.mtkpower@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.cccirpcd.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.volte_md_status.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.light@2.0 -service-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ aee_aedv.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.cccifsd.rc/vendor/ etc/init/g sm0710muxd.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ loghidlvendorservice.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ fuelgauged_init.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.wifi@1.0 -service-lazy-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.bluetooth@1.0 -service-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ ppl_agent.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.project .rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.sensor_1_0.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.mt6765.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/meta_init.connectivity.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/meta_init.project .rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/multi_init.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/factory_init.project .rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/factory_init.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.mt6762.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.mt6765.usb.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/factory_init.connectivity.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.connectivity.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.aee.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.modem.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/init.ago.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/meta_init.modem.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ hw/meta_init.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.md_apps.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.media.omx@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.volte_ua.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ nvram_daemon.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.wod.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.nvram@1.1 -sevice.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.memtrack@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.configstore@1.1 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.usb@1.1 -service-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.mtkcodecservice@1.1 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/i nit.volte_imcb.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.audio@5.0 -service-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.vibrator@1.0 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.mms@1.3 -service.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vndservicemanager.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ android.hardware.gnss@2.0 -service-mediatek.rc/vendor/ etc/init/ vendor.mediatek.hardware.pq@2.2 -service.rc/system/ apex/com.android.media.swcodec/ etc/init.rc/system/ etc/init/m dlogger.rc/system/ etc/init/ atrace.rc/system/ etc/init/m ediaextractor.rc/system/ etc/init/ surfaceflinger.rc/system/ etc/init/ ashmemd.rc/system/ etc/init/ android.system.suspend@1.0 -service.rc/system/ etc/init/u ncrypt.rc/system/ etc/init/ camerapostalgo.rc/system/ etc/init/ bootlogoupdater.rc/system/ etc/init/ art_apex_boot_integrity.rc/system/ etc/init/u sbd.rc/system/ etc/init/m odemdbfilter_client.rc/system/ etc/init/ atci_service_sys.rc/system/ etc/init/ drmserver.rc/system/ etc/init/ recovery-persist.rc/system/ etc/init/ aee_aed64.rc/system/ etc/init/ keystore.rc/system/ etc/init/ wait_for_keymaster.rc/system/ etc/init/m obile_log_d.rc/system/ etc/init/m ediaserver.rc/system/ etc/init/ hwservicemanager.rc/system/ etc/init/i nit-debug.rc/system/ etc/init/g puservice.rc/system/ etc/init/ logd.rc/system/ etc/init/i ncidentd.rc/system/ etc/init/ servicemanager.rc/system/ etc/init/ lpdumpd.rc/system/ etc/init/i dmap2d.rc/system/ etc/init/ bootstat.rc/system/ etc/init/ blank_screen.rc/system/ etc/init/ bootstat-debug.rc/system/ etc/init/ storaged.rc/system/ etc/init/ netd.rc/system/ etc/init/m ediametrics.rc/system/ etc/init/m ediadrmserver.rc/system/ etc/init/ wificond.rc/system/ etc/init/ vdc.rc/system/ etc/init/ cameraserver.rc/system/ etc/init/g sid.rc/system/ etc/init/ consyslogger.rc/system/ etc/init/ logtagd.rc/system/ etc/init/m alloc_debug_option.rc/system/ etc/init/ bootanim.rc/system/ etc/init/ logcatd.rc/system/ etc/init/ batterywarning.rc/system/ etc/init/ statsd.rc/system/ etc/init/ perfetto.rc/system/ etc/init/i nit.connectivity.rc/system/ etc/init/ flags_health_check.rc/system/ etc/init/m tpd.rc/system/ etc/init/i nit.thermald.rc/system/ etc/init/m dnsd.rc/system/ etc/init/ duraspeed.rc/system/ etc/init/ emdlogger3.rc/system/ etc/init/ audioserver.rc/system/ etc/init/ terserver.rc/system/ etc/init/ heapprofd.rc/system/ etc/init/ netdiag.rc/system/ etc/init/ bpfloader.rc/system/ etc/init/i nit.vtservice.rc/system/ etc/init/ hw/init.aee.rc/system/ etc/init/ hw/vendor_init_as_system.rc/system/ etc/init/ emdlogger5.rc/system/ etc/init/i orapd.rc/system/ etc/init/ wifi-events.rc/system/ etc/init/ tombstoned.rc/system/ etc/init/ kpoc_charger.rc/system/ etc/init/ apexd.rc/system/ etc/init/ traceur.rc/system/ etc/init/ android.hidl.allocator@1.0 -service.rc/system/ etc/init/g atekeeperd.rc/system/ etc/init/ atrace_userdebug.rc/system/ etc/init/ lmkd.rc/system/ etc/init/ rss_hwm_reset.rc/system/ etc/init/i nstalld.rc/system/ etc/init/ racoon.rc/system/ etc/init/ emdlogger2.rc/system/ etc/init/ emdlogger1.rc/system/ etc/init/ em_svr.rc/system/ etc/init/ dumpstate.rc/system/ etc/init/ aee_aed.rc/system/ etc/init/ vold.rc/root/i nit.rc/root/i nit.zygote32.rc/root/i nit.environ.rc/root/u eventd.rc/root/i nit.zygote64_32.rc/root/i nit.preload.rc/root/i nit.usb.configfs.rc/root/i nit.usb.rc
2.1 启动 当init进程启动后会调用/system/core/init/main.cpp的main()方法
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 int main(int argc, char ** argv) {if __has_feature(address_sanitizer ) __asan_set_error_report_callback(AsanReportCallback) ;if (!strcmp(basename(argv[0 ] ), "ueventd" )) {_main(argc , argv ) ; if (argc > 1 ) {if (!strcmp(argv[1 ] , "subcontext" )) {InitLogging(argv , &android ::base ::KernelLogger) ;SubcontextMain(argc , argv , &function_map ) ;if (!strcmp(argv[1 ] , "selinux_setup" )) {SetupSelinux(argv ) ; if (!strcmp(argv[1 ] , "second_stage" )) {SecondStageMain(argc , argv ) ; FirstStageMain(argc , argv ) ;
注:Android10中并不只是调用init::main,而是把部分流程性的判断放到的mian.cpp中来做,如果直接去找init.cpp中的main函数,其实是找不到入口的
2.2 一阶段启动 第一阶段init位于 system/core/init/first_stage_init.cpp的FirstStageMain方法,主要是设置umask,部分代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 int FirstStageMain(int argc , char ** argv ) {if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {InstallRebootSignalHandlers() ;() ;string , int >> errors;CHECKCALL(x ) \if (x != 0 ) errors.emplace_back(#x " failed" , errno ) ;0 );CHECKCALL(clearenv () );CHECKCALL(setenv ("PATH" , _PATH_DEFPATH , 1) );CHECKCALL(mount ("tmpfs" , "/dev" , "tmpfs" , MS_NOSUID, "mode=0755" ) );CHECKCALL(mkdir ("/dev/pts" , 0755) );CHECKCALL(mkdir ("/dev/socket" , 0755) );CHECKCALL(mount ("devpts" , "/dev/pts" , "devpts" , 0, NULL) );1 ;
2.3 二阶段启动 第二阶段init位于system/core/init/init.cpp的SecondStageMain方法,该部分负责加载.rc文件,部分代码如下
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 int SecondStageMain (int argc, char ** argv) if (REBOOT_BOOTLOADER_ON_PANIC) {InstallRebootSignalHandlers ();SetStdioToDevNull (argv);InitKernelLogging (argv);LOG (INFO) << "init second stage started!" ;keyctl_get_keyring_ID (KEY_SPEC_SESSION_KEYRING, 1 );close (open ("/dev/.booting" , O_WRONLY | O_CREAT | O_CLOEXEC, 0000 ));property_init ();process_kernel_dt (); process_kernel_cmdline (); export_kernel_boot_props ();property_set ("ro.boottime.init" , getenv ("INIT_STARTED_AT" ));property_set ("ro.boottime.init.selinux" , getenv ("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK" ));const char * avb_version = getenv ("INIT_AVB_VERSION" );if (avb_version) property_set ("ro.boot.avb_version" , avb_version);const char * force_debuggable_env = getenv ("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE" );if (force_debuggable_env && AvbHandle::IsDeviceUnlocked ()) {"true" s == force_debuggable_env;bool memcg_enabled = android::base::GetBoolProperty ("ro.boot.memcg" ,false );if (memcg_enabled) {mkdir ("/dev/memcg" , 0700 );chown ("/dev/memcg" ,AID_ROOT,AID_SYSTEM);mount ("none" , "/dev/memcg" , "cgroup" , 0 , "memory" );mkdir ("/dev/memcg/apps/" ,0755 );chown ("/dev/memcg/apps/" ,AID_SYSTEM,AID_SYSTEM);mkdir ("/dev/memcg/system" ,0550 );chown ("/dev/memcg/system" ,AID_SYSTEM,AID_SYSTEM);unsetenv ("INIT_STARTED_AT" );unsetenv ("INIT_SELINUX_TOOK" );unsetenv ("INIT_AVB_VERSION" );unsetenv ("INIT_FORCE_DEBUGGABLE" );SelinuxSetupKernelLogging ();SelabelInitialize ();SelinuxRestoreContext ();if (auto result = epoll.Open (); !result) {PLOG (FATAL) << result.error ();InstallSignalFdHandler (&epoll);property_load_boot_defaults (load_debug_prop);UmountDebugRamdisk ();fs_mgr_vendor_overlay_mount_all ();export_oem_lock_status ();StartPropertyService (&epoll);MountHandler mount_handler (&epoll) ;set_usb_controller ();const BuiltinFunctionMap function_map;set_function_map (&function_map);if (!SetupMountNamespaces ()) {PLOG (FATAL) << "SetupMountNamespaces failed" ;InitializeSubcontexts ();GetInstance ();GetInstance ();LoadBootScripts (am, sm);if (false ) DumpState ();if (android::gsi::IsGsiRunning ()) {property_set ("ro.gsid.image_running" , "1" );else {property_set ("ro.gsid.image_running" , "0" );QueueBuiltinAction (SetupCgroupsAction, "SetupCgroups" );QueueEventTrigger ("early-init" );QueueBuiltinAction (wait_for_coldboot_done_action, "wait_for_coldboot_done" );QueueBuiltinAction (MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng" );QueueBuiltinAction (SetMmapRndBitsAction, "SetMmapRndBits" );QueueBuiltinAction (SetKptrRestrictAction, "SetKptrRestrict" );QueueBuiltinAction (const BuiltinArguments& args) -> Result<Success> {for (const auto & svc : ServiceList::GetInstance ()) {Register (svc->keycodes ());Start (&epoll, HandleKeychord);return Success ();"KeychordInit" );QueueBuiltinAction (console_init_action, "console_init" );QueueEventTrigger ("init" );QueueBuiltinAction (StartBoringSslSelfTest, "StartBoringSslSelfTest" );QueueBuiltinAction (MixHwrngIntoLinuxRngAction, "MixHwrngIntoLinuxRng" );QueueBuiltinAction (InitBinder, "InitBinder" );GetProperty ("ro.bootmode" , "" );if (bootmode == "charger" ) {QueueEventTrigger ("charger" );else {QueueEventTrigger ("late-init" );QueueBuiltinAction (queue_property_triggers_action, "queue_property_triggers" );while (true ) {auto epoll_timeout = std::optional<std::chrono::milliseconds>{};if (do_shutdown && !shutting_down) {false ;if (HandlePowerctlMessage (shutdown_command)) {true ;if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running ())) {ExecuteOneCommand ();if (!(waiting_for_prop || Service::is_exec_service_running ())) {if (!shutting_down) {auto next_process_action_time = HandleProcessActions ();if (next_process_action_time) {now ());if (*epoll_timeout < 0 ms) epoll_timeout = 0 ms;if (am.HasMoreCommands ()) epoll_timeout = 0 ms;if (auto result = epoll.Wait (epoll_timeout); !result) {LOG (ERROR) << result.error ();return 0 ;
LoadBootScripts方法:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 static void LoadBootScripts(ActionManager& action_manager , ServiceList& service_list ) {CreateParser(action_manager , service_list ) ;string bootscript = GetProperty("ro.boot.init_rc" , "" ) ;if (bootscript.empty() ) {ParseConfig("/init.rc" ) ;if (!parser.ParseConfig("/system/etc/init" ) ) {_back("/system/etc/init" ) ;if (!parser.ParseConfig("/product/etc/init" ) ) {_back("/product/etc/init" ) ;if (!parser.ParseConfig("/product_services/etc/init" ) ) {_back("/product_services/etc/init" ) ;if (!parser.ParseConfig("/odm/etc/init" ) ) {_back("/odm/etc/init" ) ;if (!parser.ParseConfig("/vendor/etc/init" ) ) {_back("/vendor/etc/init" ) ;else {ParseConfig(bootscript ) ;
2.4 三阶段启动init.rc 当属性服务建立完成后,init的自身功能基本就告一段落,接下来需要来启动其他的进程。但是init进程如何其他其他进程呢?其他进程都是一个二进制文件,我们可以直接通过exec的命令方式来启动,例如 ./system/bin/init second_stage,来启动init进程的第二阶段。但是Android系统有那么多的Native进程,如果都通过传exec在代码中一个个的来执行进程,那无疑是一个灾难性的设计。
在这个基础上Android推出了一个init.rc的机制,即类似通过读取配置文件的方式,来启动不同的进程。接下来我们就来看看init.rc是如何工作的。
init.rc是一个配置文件,内部由Android初始化语言编写(Android Init Language)编写的脚本。
init.rc在手机的目录:./init.rc
启动zygote的.rc文件位于system/core/rootdir/init.rc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 // 根据系统ro.zygote属性来启动对应位数(32 /64 )进程// ro.zygote 为zygote32/zygote32_64/ zygote64_32/zygote64${ro.zygote} .rc// 启动网络相关守护进程// 启动zygote// 启动zygote_secondary
android10 ro.zygote系统默认为zygote64_32,当 ro.zygote为zygote32
import /init.zygote32.rc,对应rc文件为 system/core/rootdir/init.zygote32.rc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 /system/ bin/app_process -Xzygote / system/bin --zygote --start-system-serverclass main20 group root readproc reserved_disk660 root system 660 root systemwrite /sys/ android_power/request_state wakewrite /sys/ power /state on/dev/ cpuset/foreground/ tasks
当 ro.zygote 为zygote64_32
import /init.zygote64_32.rc,对应rc文件为 system/core/rootdir/init.zygote64_32.rc,为了兼容32位应用会同时开启64位和32位两个zygote进程,且优先使用64位。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 // 通过system/bin/ app_process64命令启动zygote/system/ bin/app_process64 -Xzygote / system/bin --zygote --start-system-server --socket-name=zygote20 660 root system // 注册socks服务660 root system/sys/ android_power/request_state wake/sys/ power/state on/dev/ cpuset/foreground/ tasks// 通过system/bin/ app_process32命令启动zygote/system/ bin/app_process32 -Xzygote / system/bin --zygote --socket-name=zygote_secondary --enable-lazy-preload20 660 root system // 注册socks服务660 root system/dev/ cpuset/foreground/ tasks
如上,可以看到服务名(进程名)是zygote,对应的可执行程序是app_processXX,而且还创建了一个名为zygote的unix domain socket,类型是stream,这个socket是为了后面IPC所用;上面可以看到还有一个zygote_secondary的进程,其实这是为了适配不同的abi型号
其中Zygote进程能够重启的地方有,以下进程杀死,Zygote重启
servicemanager进程被杀
2.5 运行/system/bin/app_processXX 接下来看看zygote启动过程,zygote对应的可执行文件就是/system/bin/app_processXX,也就是说系统启动时会执行到这个可执行文件的main()函数里
源码位于 frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp,部分代码如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 int main (int argc, char * const argv[]) AppRuntime runtime (argv[0 ], computeArgBlockSize(argc, argv)) ;int i;for (i = 0 ; i < argc; i++) {if (argv[i][0 ] != '-' ) {break ;if (argv[i][1 ] == '-' && argv[i][2 ] == 0 ) {break ;addOption (strdup (argv[i]));bool zygote = false ;bool startSystemServer = false ;bool application = false ;while (i < argc) {const char * arg = argv[i++];if (strcmp (arg, "--zygote" ) == 0 ) {true ;else if (strcmp (arg, "--start-system-server" ) == 0 ) {true ;else if (strcmp (arg, "--application" ) == 0 ) {true ;else if (strncmp (arg, "--nice-name=" , 12 ) == 0 ) {setTo (arg + 12 );else if (strncmp (arg, "--" , 2 ) != 0 ) {setTo (arg);break ;else {break ;if (zygote) {start ("com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit" , args, zygote);else if (className) {start ("com.android.internal.os.RuntimeInit" , args, zygote);else {fprintf (stderr, "Error: no class name or --zygote supplied.\n" );app_usage ();LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL ("app_process: no class name or --zygote supplied." );return 10 ;
上述代码,首先创建了一个AppRuntime的局部成员变量,然后对入参进行了解析,根据对init.zygote64_32.rc传入参数的分析,这里的zygote变量和startSystemServer的值均为true,因此在最后调用AppRuntime#start()函数时走了,而AppRuntime继承了AndroidRuntime,而子类里没有start方法,所以此处调用了AndroidRuntime::start()
2.6 AndroidRuntime::start() AndroidRuntime类位于frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 void AndroidRuntime::start(const char* className, const Vector<String8>& options, bool zygote)NULL ); if (startVm(&mJavaVM, &env, zygote) != 0 ) {return ;if (startReg(env) < 0 ) {"Unable to register all android natives\n" );return ;"java/lang/String" );NULL );1 , stringClass, NULL );NULL );NULL );0 , classNameStr);for (size_t i = 0 ; i < options.size(); ++i) {string ());NULL );1 , optionsStr);if (startClass == NULL ) {"JavaVM unable to locate class '%s'\n" , slashClassName);else {"main" ,"([Ljava/lang/String;)V" );if (startMeth == NULL ) {"JavaVM unable to find main() in '%s'\n" , className);else {
该函数启动了 Android 系统运行时库,其中它主要做了三件事:
调用startVmVM()函数启动虚拟机
调用startReg()函数注册 Android 的 Java 方法,其实在这里就是 JNI 方法
反射调用 Java 类com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit#main()方法,并把 fork zygote进程时的参数传入用来辅助初始化zygote进程
2.7 AndroidRuntime::startVm() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 int AndroidRuntime::startVm (JavaVM** pJavaVM, JNIEnv** pEnv, bool zygote) bool checkJni = false ;property_get ("dalvik.vm.checkjni" , propBuf, "" );if (strcmp (propBuf, "true" ) == 0 ) {true ;else if (strcmp (propBuf, "false" ) != 0 ) {property_get ("ro.kernel.android.checkjni" , propBuf, "" );if (propBuf[0 ] == '1' ) {true ;if (checkJni) {addOption ("-Xcheck:jni" );parseRuntimeOption ("dalvik.vm.stack-trace-file" , stackTraceFileBuf, "-Xstacktracefile:" );parseRuntimeOption ("dalvik.vm.heapstartsize" , heapstartsizeOptsBuf, "-Xms" , "4m" );parseRuntimeOption ("dalvik.vm.heapsize" , heapsizeOptsBuf, "-Xmx" , "16m" );parseRuntimeOption ("dalvik.vm.heapgrowthlimit" , heapgrowthlimitOptsBuf, "-XX:HeapGrowthLimit=" );parseRuntimeOption ("dalvik.vm.heapminfree" , heapminfreeOptsBuf, "-XX:HeapMinFree=" );parseRuntimeOption ("dalvik.vm.heapmaxfree" , heapmaxfreeOptsBuf, "-XX:HeapMaxFree=" );parseRuntimeOption ("dalvik.vm.heaptargetutilization" ,"-XX:HeapTargetUtilization=" );if (!hasFile ("/system/etc/preloaded-classes" )) {return -1 ;if (JNI_CreateJavaVM (pJavaVM, pEnv, &initArgs) < 0 ) {ALOGE ("JNI_CreateJavaVM failed\n" );return -1 ;
2.8 AndroidRuntime::startReg() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 int AndroidRuntime::startReg(JNIEnv* env ) SetCreateThreadFunc((android_create_thread_fn ) javaCreateThreadEtc);PushLocalFrame(200) ;if (register_jni_procs(gRegJNI , NELEM(gRegJNI ) , env) < 0 ) {PopLocalFrame(NULL) ;1 ;PopLocalFrame(NULL) ;0 ;
2.9 进入java世界,com.android.internal.os.ZygoteInit#main() 源码位于frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 public static void main(String argv[]) {try {"ZygoteInit" );boolean startSystemServer = false ;String socketName = "zygote" ;String abiList = null ;for (int i = 1 ; i < argv.length; i++) {if ("start-system-server" .equals(argv[i])) {true ;else if (argv[i].startsWith(ABI_LIST_ARG)) {else if (argv[i].startsWith(SOCKET_NAME_ARG)) {else {throw new RuntimeException ("Unknown command line argument: " + argv[i]);if (abiList == null ) {throw new RuntimeException ("No ABI list supplied." );"ZygotePreload" );"PostZygoteInitGC" );false );if (startSystemServer) {"Accepting command socket connections" );catch (MethodAndArgsCaller caller) {catch (Throwable ex) {"Zygote died with exception" , ex);throw ex;
在这个初始化过程中,做了不少准备工作,更加详细的过程请阅读上述代码注释和源码,我们这里总结以下我们需要着重关注的几件事:
调用ZygoteServer#registerServerSocket()方法创建一个名为zygote的 Socket 资源
调用preload预加载资源
调用ZygoteInit#starSystemServer()方法启动system_server进程
调用ZygoteInit#runSelectLoop()方法循环接受 Socket 连接,在这里开始和 AMS 搭上边,其实这里就是循环等待 AMS 的连接和命令,更加详细的过程在下文中分析。
2.10 ZygoteInit.registerZygoteSocket() Socket 是 IPC 通信的一种方式,该 Socket 资源在后期被用在和 AMS 等服务进行进程间通信
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 private static void registerZygoteSocket(String socketName) {if (sServerSocket == null ) {int fileDesc;final String fullSocketName = ANDROID_SOCKET_PREFIX + socketName;try {String env = System.getenv(fullSocketName);Integer .parseInt(env);catch (RuntimeException ex) {throw new RuntimeException (fullSocketName + " unset or invalid" , ex);try {new FileDescriptor();new LocalServerSocket(fd);catch (IOException ex) {throw new RuntimeException ("Error binding to local socket '" + fileDesc + "'" , ex);
2.11 ZygoteInit.preload() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 static void preload() {// 预加载位于/system/ etc/preloaded-classes文件中的类// 预加载资源,包含drawable和color资源// 预加载OpenGL// 通过System.loadLibrary()方法,// 预加载"android" ,"compiler_rt" ,"jnigraphics" 这3 个共享库// 预加载 文本连接符资源// 仅用于zygote进程,用于内存共享的进程
执行Zygote进程的初始化,对于类加载,采用反射机制Class.forName()方法来加载。对于资源加载,主要是 com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_drawables和com.android.internal.R.array.preloaded_color_state_lists,在应用程序中以com.android.internal.R.xxx开头的资源,便是此时由Zygote加载到内存的
2.11 ZygoteInit.startSystemServer() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 private static boolean startSystemServer(String abiList, String socketName)RuntimeException {String args[] = {"--setuid=1000" ,"--setgid=1000" ,"--setgroups=1001,1002,1003,1004,1005,1006,1007,1008,1009,1010,1018,1021,1032,3001,3002,3003,3006,3007,3009,3010" ,"--capabilities=" + capabilities + "," + capabilities,"--nice-name=system_server" , "--runtime-args" ,"com.android.server.SystemServer" ,null ;int pid;try {new ZygoteConnection.Arguments(args);null ,catch (IllegalArgumentException ex) {throw new RuntimeException (ex);if (pid == 0 ) {if (hasSecondZygote(abiList)) {return true ;
这个方法先准备参数,然后fork新进程,对于有两个zygote进程情况,需等待第2个zygote创建完成
2.12 Zygote.forkSystemServer() 源码位于frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/Zygote.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public static int forkSystemServer (int uid, int gid, int [] gids, int debugFlags, int [][] rlimits, long permittedCapabilities, long effectiveCapabilities) preFork ();int pid = nativeForkSystemServer (if (pid == 0 ) {setTracingEnabled (true );postForkCommon ();return pid;
nativeForkSystemServer()方法在AndroidRuntime.cpp中注册的,调用com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp中的register_com_android_internal_os_Zygote()方法建立native方法的映射关系,所以接下来进入如下方法
源码位于 frameworks/base/core/jni/com_android_internal_os_Zygote.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkSystemServer ( JNIEnv* env, jclass, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray gids, jint debug_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jlong permittedCapabilities, jlong effectiveCapabilities) pid_t pid = ForkAndSpecializeCommon (env, uid, gid, gids,NULL , NULL , true , NULL ,NULL , NULL );if (pid > 0 ) {int status;if (waitpid (pid, &status, WNOHANG) == pid) {RuntimeAbort (env, __LINE__, "System server process has died. Restarting Zygote!" );return pid;
当system_server进程创建失败时,将会重启zygote进程。这里需要注意,对于Android 5.0以上系统,有两个zygote进程,分别是zygote、zygote64两个进程,system_server的父进程,一般来说64位系统其父进程是zygote64进程
当kill system_server进程后,只重启zygote64和system_server,不重启zygote;
当kill zygote64进程后,只重启zygote64和system_server,也不重启zygote;
当kill zygote进程,则重启zygote、zygote64以及system_server。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 static pid_t ForkAndSpecializeCommon(JNIEnv* env, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray javaGids,bool is_system_server, jintArray fdsToClose,if (pid == 0 ) {if (!is_system_server) {int rc = createProcessGroup(uid, getpid());int rc = setresgid(gid, gid, gid);if (se_info_c_str == NULL && is_system_server) {"system_server" ;if (se_info_c_str != NULL ) {NULL : instructionSet);else if (pid > 0 ) {return pid;int fork() {self = __get_thread();self ->invalidate_cached_pid();int result = syscall(__NR_clone, FORK_FLAGS, NULL , NULL , NULL , &(self ->tid));if (result == 0 ) {self ->set_cached_pid(gettid());else {self ->set_cached_pid(parent_pid);return result;
到此system_server进程已完成了创建的所有工作,接下来开始了system_server进程的真正工作。在前面startSystemServer()方法中,zygote进程执行完forkSystemServer()后,新创建出来的system_server进程便进入handleSystemServerProcess()方法
2.15 ZygoteInit.handleSystemServerProcess() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 private static void handleSystemServerProcess(throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {if (parsedArgs.niceName != null ) {final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH" );if (systemServerClasspath != null ) {if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null ) {String [] args = parsedArgs.remainingArgs;if (systemServerClasspath != null ) {String [] amendedArgs = new String [args.length + 2 ];0 ] = "-cp" ;1 ] = systemServerClasspath;0 , amendedArgs, 2 , parsedArgs.remainingArgs.length);null , args);else {null ;if (systemServerClasspath != null ) {new PathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, ClassLoader.getSystemClassLoader());
2.16 RuntimeInit.zygoteInit() 源码位于frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/RuntimeInit.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion , String[] argv , ClassLoader classLoader ) Trace .Begin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "RuntimeInit" ) ;LogStreams() ; Init() ; ZygoteInit() ; Init(targetSdkVersion , argv , classLoader ) ; private static final void commonInit() {Thread .DefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new UncaughtHandler() );TimezoneGetter .Instance(new TimezoneGetter() {Id() {SystemProperties ."persist.sys.timezone" );TimeZone .Default(null ) ;LogManager .LogManager() .reset() ;new AndroidConfig() ;DefaultUserAgent() ;System .Property("http.agent" , userAgent ) ;NetworkManagementSocketTagger .() ;private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion , String[] argv , ClassLoader classLoader ) SetExitWithoutCleanup(true ) ;VMRuntime .Runtime() .setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f) ;VMRuntime .Runtime() .setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion ) ;try {new Arguments(argv ) ; Trace .End(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER) ;StaticMain(args .startClass , args .startArgs , classLoader ) ;private static void invokeStaticMain(String className , String[] argv , ClassLoader classLoader ) Class .for Name(className , true , classLoader ) ; ... Method m;try {Method("main" , new Class[] { String[].class }) ; ... } catch (SecurityException ex) { ... }new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m , argv ) ;
重点看最后一个方法,通过反射获取SystemServer类的main方法参数,然后抛出MethodAndArgsCaller异常;但是抛出异常后怎么弄呢,我们知道一个方法抛异常,会一直走到调用方法,直到一个方法捕获了异常,这里就是开头讲的,在ZygoteInit.main方法捕获了异常然后去执行
2.17 ZygoteInit.main() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public static void main (String argv[]) try {if (startSystemServer) {startSystemServer (abiList, socketName);catch run ();catch closeServerSocket ();throw ex;
但是为啥没有直接在startSystemServer()或者上面的方法中直接调用SystemServer类的main方法,而是通过抛异常的方式处理呢?
我们知道,当一个函数抛出异常后,这个异常会依次传递给调用它的函数,直到这个异常被捕获,如果这个异常一直没有被处理,最终就会引起程序的崩溃。
程序都是由一个个函数组成的(除了汇编程序),c/c++/java/…等高级语言编写的应用程序,在执行的时候,他们都拥有自己的栈空间(是一种先进后出的内存区域),用于存放函数的返回地址和函数的临时数据,每调用一个函数时,就会把函数的返回地址和相关数据压入栈中,当一个函数执行完后,就会从栈中弹出,cpu会根据函数的返回地址,执行上一个调用函数的下一条指令。
所以,在抛出异常后,如果异常没有在当前的函数中捕获,那么当前的函数执行就会异常的退出,从应用程序的栈弹出,并将这个异常传递给上一个函数,直到异常被捕获处理,否则,就会引起程序的崩溃。
因此,这里通过抛异常的方式启动主要是清理应用程序栈中ZygoteInit.main以上的函数栈帧,以实现当相应的main函数退出时,能直接退出整个应用程序
2.18 ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller.run() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception implements Runnable {private final Method mMethod;private final String [] mArgs;public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String [] args) {public void run() {try {null , new Object [] { mArgs });catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new RuntimeException (ex);catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {Throwable cause = ex.getCause();if (cause instanceof RuntimeException ) {throw (RuntimeException ) cause;else if (cause instanceof Error ) {throw (Error ) cause;throw new RuntimeException (ex);
可以看到这里根据传递过来的参数,可知此处通过反射机制调用的是SystemServer.main()方法;到此,总算是进入到了SystemServer类的main()方法
2.19 SystemServer.main() 源码位于 frameworks/base/services/java/com/android/server/SystemServer.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 public static void main (String [] args) new SystemServer ().run ();private void run () try {if (System.currentTimeMillis () < EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME) {setCurrentTimeMillis (EARLIEST_SUPPORTED_TIME);set ("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2" , VMRuntime.getRuntime ().vmLibrary ());getRuntime ().clearGrowthLimit ();getRuntime ().setTargetHeapUtilization (0.8f );ensureFingerprintProperty ();setUserRequired (true );setShouldDefuse (true );disableBackgroundScheduling (true );setMaxThreads (sMaxBinderThreads);Process .setThreadPriority (Process .THREAD_PRIORITY_FOREGROUND);Process .setCanSelfBackground (false );prepareMainLooper ();loadLibrary ("android_servers" );performPendingShutdown ();createSystemContext ();new SystemServiceManager (mSystemContext);addService (SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);traceEnd (Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);try {startBootstrapServices ();startCoreServices ();startOtherServices ();catch throw ex;traceEnd (Trace.TRACE_TAG_SYSTEM_SERVER);loop ();throw new RuntimeException ("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited" );
至此system_server已启动完成,大致流程如下:
zygote进程通过Zygote.forkSystemServer —> fork.fork()创建system server进程
调用ZygoteInit.handleSystemServerProcess方法设置当前进程名为”system_server”,执行dex优化操作,一些属性的初始化,设置binder线程
通过抛出MethodAndArgsCaller异常,回到ZygoteInit.main(),在try catch中执行MethodAndArgsCaller.run;在这里通过反射执行SystemServer.main()方法
在SystemServer.run方法中做一些设置,比如初始化系统上下文 ,创建SystemServiceManager,启动引导服务,启动核心服务,启动其他服务
最后调用Looper.loop(),不断的从消息队列取出消息处理(Looper#loop()方法中调用的是MessageQueue#next(),该方法中使用死循环 + Linuxepoll机制持续运行程序)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 system server进程和zygote进程可以说是Android世界中的两大最重要的进程,离开其中之一基本上系统就玩完了;基本上在Java Framework中的大多数服务都是在system server进程中一个线程的方式存在的,如下:BatteryService 电池管理服务BluetoothService 蓝牙服务Android 中的通知栏和状态栏在一起,只是界面上前者在左边,后者在右边BackupManagerService 系统备份服务DiskStatsService 磁盘统计服务
2.20 ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop() 在2.9中ZygoteInit.main()方法开启system_server后,执行runSelectLoop()方法,进入循环监听事件
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();add (sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());add (null );while (true ) {new StructPollfd[fds.size ()];for (int i = 0 ; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {new StructPollfd();get (i);short ) POLLIN;try {-1 );catch (ErrnoException ex) {for (int i = pollFds.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i) {if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0 ) {continue ;if (i == 0 ) {add (newPeer);add (newPeer.getFileDesciptor()); else {boolean done = peers.get (i).runOnce();if (done) {
2.21 ZygoteInit.acceptCommandPeer 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 private static ZygoteConnection acceptCommandPeer (String abiListtry {return new ZygoteConnection(sServerSocket.accept(), abiList);catch (IOException ex) {
2.22 ZygoteConnection.runOnce 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 boolean runOnce() throws ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller {null ;try {catch (IOException ex) {return true ;try {new Arguments(args);catch (Exception e) {try {if (pid == 0 ) {null ;return true ;else {null ;return handleParentProc (pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs) finally {
至此Zygote启动完成,开启循环
没有连接请求时会进入休眠状态,当有创建新进程的连接请求时,唤醒Zygote进程,创建Socket通道ZygoteConnection,然后执行ZygoteConnection的runOnce()方法。
Zygote启动流程如下:
解析init.zygote64_32.rc中的参数,创建AppRuntime并调用AppRuntime.start()方法
调用AndroidRuntime的startVM()方法创建虚拟机,再调用startReg()注册JNI函数
通过JNI方式调用ZygoteInit.main(),第一次进入Java世界
registerZygoteSocket()建立socket通道,zygote作为通信的服务端,用于响应客户端请求
preload()预加载通用类、drawable和color资源、openGL以及共享库以及WebView,用于提高app启动效率
通过startSystemServer(),fork得力帮手system_server进程,也是Java Framework的运行载体
调用runSelectLoop(),随时待命,当接收到请求创建新进程请求时立即唤醒并执行相应工作
3. Zygote进程是如何fork一个APP进程的 创建一个线程大家肯定非常熟悉了,继承Thread,实现Runnable接口或者Callable接口;但是线程没有独立的地址空间,而是与所在进程共享内存,其实从Linux角度看,进程线程都是一个task_struct结构体,除了是否共享资源外,并没有其他本质的区别。
但是创建进程可能就没有那么熟悉了,每个APP可能运行在一个进程,也可能在多个进程,这些进程拥有自己独立的资源;然而这些进程都是由Zygote进程fork出来的,再往前一步其实是system server进程使用LocalSocket去通知zygote进程,然后zygote去fork一个子进程,也就是APP进程(更往前一步就是APP进程使用Binder机制去通知system server进程中的ActivityManagerService),注意这里是子进程,不是子线程
大体流程:
app_process作为zygote server通过local socket处理进程创建请求,zygote server是在ZygoteInit.main函数里调用ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop监听。
接收到zygote client的fork请求之后,调用ZygoteConnection.runOnce,调用Zygote.forkAndSpecialize创建新进程
进程创建之后,由ZygoteConnection.handleParentProc来初始化进程,最终会调用ActivityThread.main函数
ActivityThread.main -> ActivityThread.attach -> ActivityThread.bindApplication -> Activity.handleBindApplication,handleBindApplication会初始化BaseDexClassLoader。
类的加载经过了ClassLoader.loadClass->BaseDexClassLoader.findClass->DexPathList.findClass->DexFile.loadClassBinaryName->DexFile.defineClassNative->DexFile_defineClassNative(art/runtime/native/dalvik_system_DexFile.cc)
3.1 APP进程创建流程
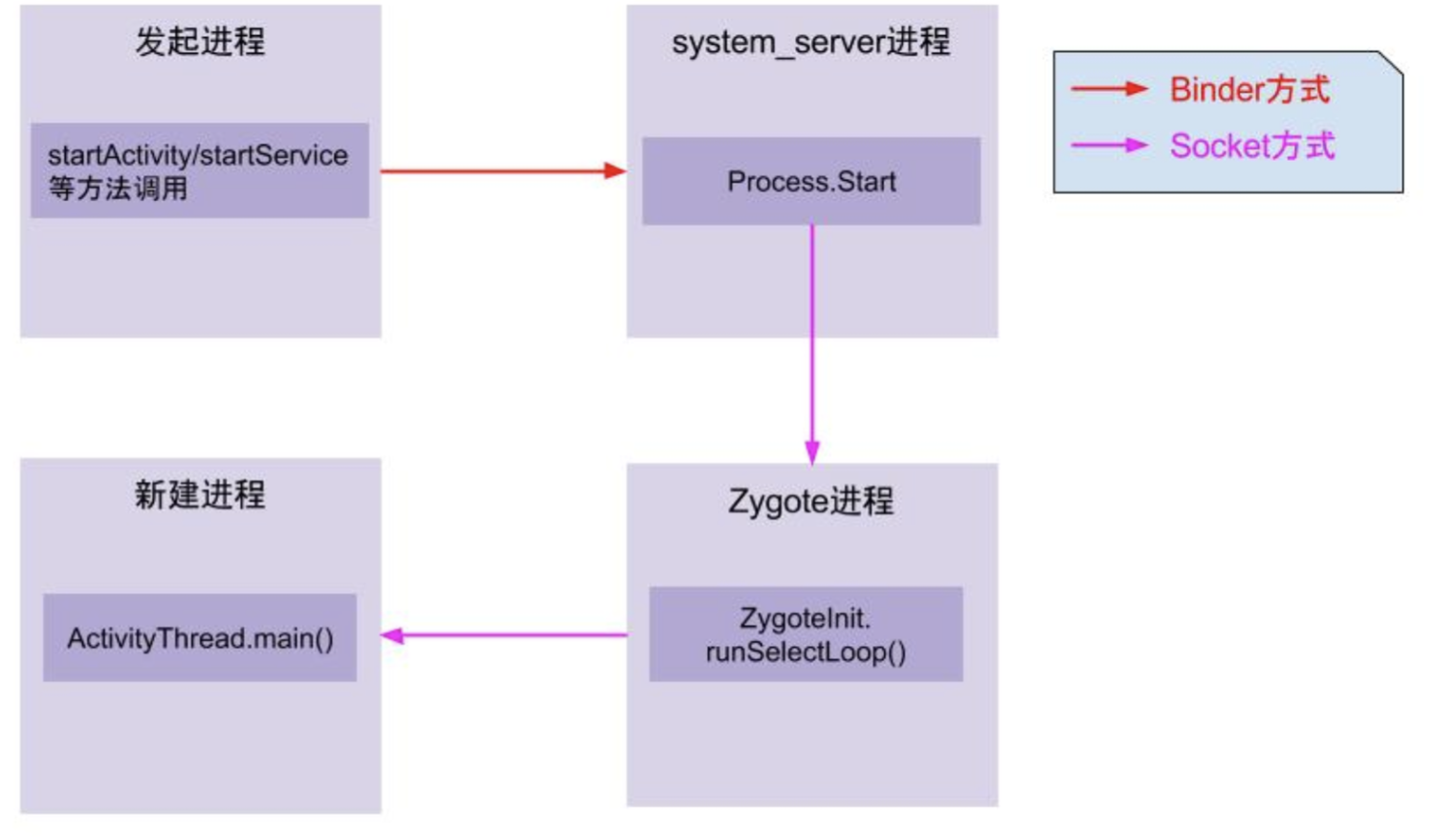
不管从桌面启动应用还是应用内启动其它应用,如果这个应用所在进程不存在的话,都需要发起进程通过Binder机制告诉system server进程的AMS
system server进程的AMS调用Process.start()方法,通过socket向zygote进程发送创建新进程的请求
在zygote进程的ZygoteInit.main方法中,有一个runSelectLoop循环体,通过acceptCommandPeer方法获取链接过来的客户端,再通过runOnce方法去创建进程
新的进程执行handleChildProc方法,最后通过反射调用ActivityThread.main()方法,这样一个新的APP进程就创建完成了
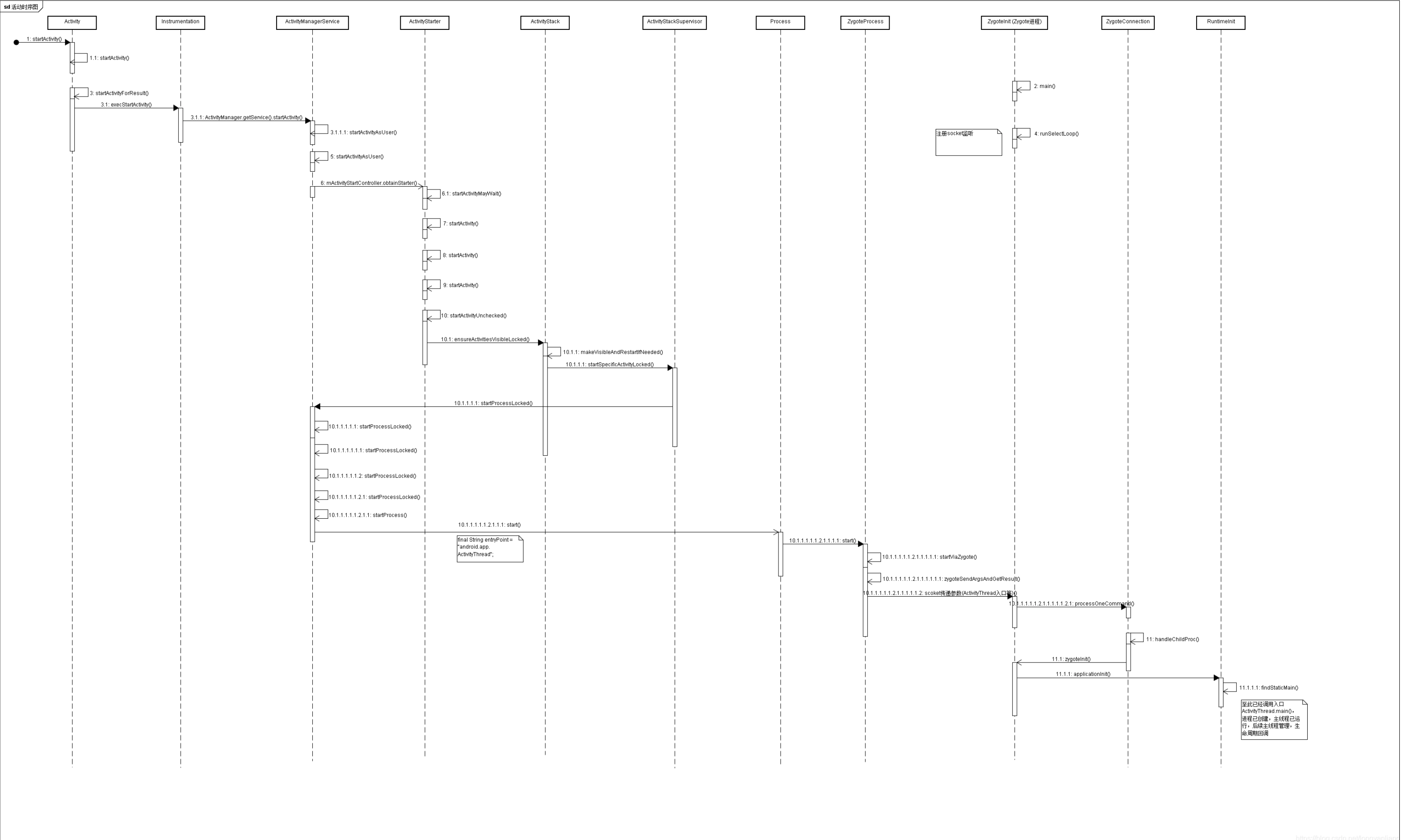
3.2 APP启动第三方应用 3.2.1 startActivity 当你在桌面启动一个应用或者在一个APP内启动一个应用,本质都是一样的,因为Android手机桌面其实就是一个APP(这点可参考Android之Activity启动流程源码深入解析),两种方式经过层层调用之后都会走到ActivityStackSupervisor.startSpecificActivityLocked方法,判断如果对方进程不存在,就需要去创建一个进程
3.2.2 startService 调用startService启动一个服务,该方法经过层层调用最终会走到ActiveServices.bringUpServiceLocked方法,如果判断对方进程不存在也会去创建一个新进程
3.2.3 sendBroadcast 调用sendBroadcast方法去发送一个广播,经过层层调用后走到BroadcastQueue.processNextBroadcast方法,也会判断BroadcastReceiver所在进程不存在就需要去创建进程
3.2.4 ContentResolver.query 在ContentProvider的处理过程中,ContentResolver.query方法经过层层调用会走到ActivityManagerService.getContentProviderImpl方法,判断ContentProvider所在的进程不存在就会创建新进程
3.3 System Server请求创建进程 ActivityManagerService简称为AMS
上述四种途径最终都会走到AMS.startProcessLocked()方法
3.3.1 AMS.startProcessLocked() 源码位于frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/am/ActivityManagerService.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName,boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags,String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName, boolean allowWhileBooting,boolean isolated, boolean keepIfLarge) {return startProcessLocked(processName, info, knownToBeDead, intentFlags, hostingType,0 , keepIfLarge,null , null , null ,null );final ProcessRecord startProcessLocked(String processName, ApplicationInfo info,boolean knownToBeDead, int intentFlags, String hostingType, ComponentName hostingName,boolean allowWhileBooting, boolean isolated, int isolatedUid, boolean keepIfLarge,String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String [] entryPointArgs, Runnable crashHandler) {long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();if (!isolated) {"startProcess: after getProcessRecord" );if ((intentFlags & Intent.FLAG_FROM_BACKGROUND) != 0 ) {if (mAppErrors.isBadProcessLocked(info)) {return null ;else {if (mAppErrors.isBadProcessLocked(info)) {if (app != null ) {false ;else {null ;if (app != null && app.pid > 0 ) {if ((!knownToBeDead && !app.killed) || app.thread == null ) {"startProcess: done, added package to proc" );return app;"startProcess: bad proc running, killing" );true , true );"startProcess: done killing old proc" );String hostingNameStr = hostingName != null null ;if (app == null ) {"startProcess: creating new process record" );if (app == null ) {return null ;"startProcess: done creating new process record" );else {"startProcess: added package to existing proc" );if (!mProcessesReadyif (!mProcessesOnHold.contains(app)) {add (app);if (DEBUG_PROCESSES) Slog.v(TAG_PROCESSES,"System not ready, putting on hold: " + app);"startProcess: returning with proc on hold" );return app;"startProcess: stepping in to startProcess" );"startProcess: done starting proc!" );return (app.pid != 0 ) ? app : null ;
经过上面重重判断后决定需要创建进程,继续走到startProcessLocked方法,这个方法在AMS里有4个重载的方法
其中的hostingType参数有”activity”,”service”,”broadcast”,”content provider”四个值
3.3.2 继续调用AMS.startProcessLocked() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 private final void startProcessLocked (ProcessRecord app, String hostingType, String hostingNameStr, String abiOverride, String entryPoint, String [] entryPointArgs) long startTime = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime ();if (app.pid > 0 && app.pid != MY_PID) {checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: removing from pids map" );synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {remove (app.pid);removeMessages (PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG, app);checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: done removing from pids map" );setPid (0 );remove (app);checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: starting to update cpu stats" );updateCpuStats ();checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: done updating cpu stats" );try {try {final int userId = UserHandle.getUserId (app.uid);getPackageManager ().checkPackageStartable (app.info.packageName, userId);catch throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException ();int uid = app.uid;int [] gids = null;int mountExternal = Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_NONE;if (!app.isolated) {int [] permGids = null;try {checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: getting gids from package manager" );final IPackageManager pm = AppGlobals.getPackageManager ();getPackageGids (app.info.packageName,getService (getExternalStorageMountMode (uid,catch throw e.rethrowAsRuntimeException ();if (ArrayUtils.isEmpty (permGids)) {new int [2 ];else {new int [permGids.length + 2 ];arraycopy (permGids, 0 , gids, 2 , permGids.length);0 ] = UserHandle.getSharedAppGid (UserHandle.getAppId (uid));1 ] = UserHandle.getUserGid (UserHandle.getUserId (uid));checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: building args" );Process .ProcessStartResult startResult = Process .start (entryPoint,checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: returned from zygote!" );traceEnd (Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);setPid (startResult.pid);false ;false ;false ;checkTime (startTime, "startProcess: starting to update pids map" );synchronized (mPidsSelfLocked) {if ((oldApp = mPidsSelfLocked.get (startResult.pid)) != null && !app.isolated) {cleanUpApplicationRecordLocked (oldApp, false , false , -1 ,true );this .mPidsSelfLocked.put (startResult.pid, app);if (isActivityProcess) {obtainMessage (PROC_START_TIMEOUT_MSG);sendMessageDelayed (msg, startResult.usingWrappercheckTime (startTime, "startProcess: done updating pids map" );catch getAppId (app.uid), false ,false , true , false , false , UserHandle.getUserId (app.userId), "start failure" );
这个方法中最重要的就是通过Process.start来创建应用进程;原理是通过socket向Zygote进程发送创建新进程的请求;Zygote进程启动后有一个runSelectLoop循环,当收到客户端请求便会执行ZygoteConnection.runOnce()方法,再经过层层调用后fork出新的应用进程,创建新进程后将ActivityThread类加载到新进程,并调用ActivityThread.main()方法
3.3.3 Process.start() 源码位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Process.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 public static final ProcessStartResult start (final String processClass, final String niceName, int uid, int gid, int [] gids, int debugFlags, int mountExternal, int targetSdkVersion, String seInfo, String abi, String instructionSet, String appDataDir, String [] zygoteArgs) try {return startViaZygote (processClass, niceName, uid, gid, gids,catch throw new RuntimeException ("Starting VM process through Zygote failed" , ex);
3.3.4 Process.startViaZygote() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote(final String processClass,final String niceName,final int uid, final int gid,final int [] gids,int debugFlags, int mountExternal,int targetSdkVersion,String seInfo,String abi,String instructionSet,String appDataDir,String [] extraArgs)throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {synchronized (Process.class) {String > argsForZygote = new ArrayList<String >();add ("--runtime-args" );add ("--setuid=" + uid);add ("--setgid=" + gid);if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_JNI_LOGGING) != 0 ) {add ("--enable-jni-logging" );if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_SAFEMODE) != 0 ) {add ("--enable-safemode" );if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_DEBUGGER) != 0 ) {add ("--enable-debugger" );if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_CHECKJNI) != 0 ) {add ("--enable-checkjni" );if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_GENERATE_DEBUG_INFO) != 0 ) {add ("--generate-debug-info" );if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ALWAYS_JIT) != 0 ) {add ("--always-jit" );if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_NATIVE_DEBUGGABLE) != 0 ) {add ("--native-debuggable" );if ((debugFlags & Zygote.DEBUG_ENABLE_ASSERT) != 0 ) {add ("--enable-assert" );if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_DEFAULT) {add ("--mount-external-default" );else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_READ) {add ("--mount-external-read" );else if (mountExternal == Zygote.MOUNT_EXTERNAL_WRITE) {add ("--mount-external-write" );add ("--target-sdk-version=" + targetSdkVersion);if (gids != null && gids.length > 0 ) {new StringBuilder();append ("--setgroups=" );int sz = gids.length;for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) {if (i != 0 ) {append (',' );append (gids[i]);add (sb.toString());if (niceName != null ) {add ("--nice-name=" + niceName);if (seInfo != null ) {add ("--seinfo=" + seInfo);if (instructionSet != null ) {add ("--instruction-set=" + instructionSet);if (appDataDir != null ) {add ("--app-data-dir=" + appDataDir);add (processClass);if (extraArgs != null ) {for (String arg : extraArgs) {add (arg);return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult(openZygoteSocketIfNeeded(abi), argsForZygote);
3.3.5 Process.zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 private static ProcessStartResult zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult ( ZygoteState zygoteState, ArrayList<String > args) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {try {int sz = args.size ();for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) {if (args.get (i).indexOf ('\n' ) >= 0 ) {throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx ("embedded newlines not allowed" );final BufferedWriter writer = zygoteState.writer;final DataInputStream inputStream = zygoteState.inputStream;write (Integer.toString (args.size ()));newLine ();for (int i = 0 ; i < sz; i++) {String arg = args.get (i);write (arg);newLine ();flush ();new ProcessStartResult ();readInt ();readBoolean ();if (result.pid < 0 ) {throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx ("fork() failed" );return result;catch close ();throw new ZygoteStartFailedEx (ex);
这个方法作用就是通过Socket向zygote进程发送一个参数列表,然后就进入阻塞状态,直到远程Socket服务端返回新创建的进程pid
说到这里我们好像没有见到Socket的影子,只见到了ZygoteState这么一个东西,那它怎么来的呢,可以看见它是上一个方法startViaZygote调用zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult方法传过来的参数,就是这么一句话
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private static ProcessStartResult startViaZygote (final String processClass, final String niceName, final int uid, final int gid, final int [] gids, int debugFlags, int mountExternal, int targetSdkVersion, String seInfo, String abi, String instructionSet, String appDataDir, String [] extraArgs) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {synchronized (Process .class) { return zygoteSendArgsAndGetResult (openZygoteSocketIfNeeded (abi), argsForZygote);
3.3.6 Process.openZygoteSocketIfNeeded() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 private static ZygoteState open ZygoteSocketIfNeeded(String abi ) throws ZygoteStartFailedEx {if (primaryZygoteState == null || primaryZygoteState.isClosed() ) {try {ZygoteState .new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to primary zygote" , ioe ) ;if (primaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {if (secondaryZygoteState == null || secondaryZygoteState.isClosed() ) {try {ZygoteState .new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Error connecting to secondary zygote" , ioe ) ;if (secondaryZygoteState.matches(abi)) {new ZygoteStartFailedEx("Unsupported zygote ABI: " + abi ) ;
这个方法会根据当前的abi来选择与zygote还是zygote64进行通信,在init进程解析rc文件的时候,会根据abi型号创建两个zygote;该方法最终会返回一个ZygoteState,它是Process的静态内部类,具体连接实现在ZygoteState.connect方法中
3.3.7 Process.ZygoteState() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 public static class ZygoteState {final LocalSocket socket;final DataInputStream inputStream;final BufferedWriter writer;final List<String > abiList;boolean mClosed;private ZygoteState (LocalSocket socket, DataInputStream inputStream, BufferedWriter writer, List<String > abiList) this .socket = socket;this .inputStream = inputStream;this .writer = writer;this .abiList = abiList;public static ZygoteState connect (String socketAddress) throws IOException final LocalSocket zygoteSocket = new LocalSocket ();try {connect (new LocalSocketAddress (socketAddress,new DataInputStream (zygoteSocket.getInputStream ());new BufferedWriter (new OutputStreamWriter (getOutputStream ()), 256 );catch try {close ();catch throw ex;String abiListString = getAbiList (zygoteWriter, zygoteInputStream);i ("Zygote" , "Process: zygote socket opened, supported ABIS: " + abiListString);return new ZygoteState (zygoteSocket, zygoteInputStream, zygoteWriter,asList (abiListString.split ("," )));boolean matches (String abi) return abiList.contains (abi);public void close () try {close ();catch e (LOG_TAG,"I/O exception on routine close" , ex);true ;boolean isClosed () return mClosed;
可以看到这里是通过LocalSocket进行进程间通信;这种通信的双方一般是Native层的server端,Framework层的Client端,中间涉及到jni调用。
而Android中的LocalSocket是基于UNIX-domain Socket的,UNIX-domain Socket是在Socket的基础上衍生出来的一种IPC通信机制,因此LocalSocket解决的是同一台主机上不同进程间互相通信的问题。其相对于网络通信使用的socket不需要经过网络协议栈,不需要打包拆包、计算校验,自然的执行效率也高。与大名鼎鼎的binder机制作用一样,都在Android系统中作为IPC通信手段被广泛使用;一般由LocalSocket(Client)和LocalServerSocket(Server)组成通信双方。
那么在本文中AMS所在的system-server进程就充当了Client,zygote进程充当Server,因为zygote进程在创建的时候会在ZygoteInit.main方法中调用ZygoteInit.registerZygoteSocket方法,会实例化一个LocalServerSocket,并且在ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop方法中不停的获取客户端的请求
3.4 Zygote接收到请求 3.4.1 ZygoteInit.main() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public static void main (String argv[]) try {registerZygoteSocket (socketName); runSelectLoop (abiList); catch run ();catch closeServerSocket ();throw ex;
3.4.2 ZygoteInit.runSelectLoop() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 private static void runSelectLoop(String abiList) throws MethodAndArgsCaller {new ArrayList<FileDescriptor>();new ArrayList<ZygoteConnection>();add (sServerSocket.getFileDescriptor());add (null );while (true ) {new StructPollfd[fds.size ()];for (int i = 0 ; i < pollFds.length; ++i) {new StructPollfd();get (i);short ) POLLIN;try {-1 );catch (ErrnoException ex) {for (int i = pollFds.length - 1 ; i >= 0 ; --i) {if ((pollFds[i].revents & POLLIN) == 0 ) {continue ;if (i == 0 ) {add (newPeer);add (newPeer.getFileDesciptor()); else {boolean done = peers.get (i).runOnce();if (done) {
这里通过acceptCommandPeer方法获取连接过来的客户端,然后执行ZygoteConnection.runOnce方法处理请求
3.4.3 ZygoteConnection.runOnce() 源码位于 frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteConnection.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 String args[];null ;try {catch (IOException ex) {return true ;try {new Arguments (args);catch (Exception e) {try {if (pid == 0 ) {null ;new Stderr );return true ;else {null ;return handleParentProc(pid, descriptors, serverPipeFd, parsedArgs);
这里先解析客户端发送过来的参数列表,然后调用Zygote.forkAndSpecialize方法
3.4.4 Zygote.forkAndSpecialize() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 private static final ZygoteHooks VM_HOOKS = new ZygoteHooks ();public static int forkAndSpecialize (int uid, int gid, int [] gids, int debugFlags, int [][] rlimits, int mountExternal, String seInfo, String niceName, int [] fdsToClose, String instructionSet, String appDataDir) preFork ();int pid = nativeForkAndSpecialize (postForkCommon ();return pid;
这里在fork新进程的时候会先调用 VM_HOOKS.preFork()
3.4.5 ZygoteHooks.preFork() 1 2 3 4 5 public void preFork() {Daemons .() ; UntilAllThreadsStopped() ; PreFork() ;
这个方法的主要目的是停止zygote进程的四个daemon子线程,分别是ReferenceQueueDaemon,FinalizerDaemon,FinalizerWatchdogDaemon,HeapTaskDaemon;直到zygote是是单线程,以便于提高fork效率;
fork新进程是调用native方法,经过jni调用
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 static jint com_android_internal_os_Zygote_nativeForkAndSpecialize ( JNIEnv* env, jclass, jint uid, jint gid, jintArray gids, jint debug_flags, jobjectArray rlimits, jint mount_external, jstring se_info, jstring se_name, jintArray fdsToClose, jstring instructionSet, jstring appDataDir) 0 ;if (uid == AID_BLUETOOTH) {1 LL << CAP_WAKE_ALARM);return ForkAndSpecializeCommon (env, uid, gid, gids, debug_flags, rlimits, capabilities, capabilities, mount_external, se_info, se_name, false , fdsToClose, instructionSet, appDataDir)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 static pid_t ForkAndSpecializeCommon (JNIEnv* env, uid_t uid, gid_t gid, jintArray javaGids, jint debug_flags, jobjectArray javaRlimits, jlong permittedCapabilities, jlong effectiveCapabilities, jint mount_external, jstring java_se_info, jstring java_se_name, bool is_system_server, jintArray fdsToClose, jstring instructionSet, jstring dataDir) SetSigChldHandler ();pid_t pid = fork();if (pid == 0 ) { DetachDescriptors (env, fdsToClose); if (!is_system_server) {int rc = createProcessGroup (uid, getpid ());SetGids (env, javaGids); SetRLimits (env, javaRlimits); int rc = setresgid (gid, gid, gid);setresuid (uid, uid, uid);SetCapabilities (env, permittedCapabilities, effectiveCapabilities);SetSchedulerPolicy (env); selinux_android_setcontext (uid, is_system_server, se_info_c_str, se_name_c_str);if (se_info_c_str == NULL && is_system_server) {"system_server" ;if (se_info_c_str != NULL ) {SetThreadName (se_name_c_str); UnsetSigChldHandler ();CallStaticVoidMethod (gZygoteClass, gCallPostForkChildHooks, debug_flags,NULL : instructionSet);else if (pid > 0 ) {return pid;
这里会通过fork()方法创建进程
3.4.8 fork.fork() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 int fork() {self = __get_thread();self ->invalidate_cached_pid();int result = syscall(__NR_clone, FORK_FLAGS, NULL , NULL , NULL , &(self ->tid));if (result == 0 ) {self ->set_cached_pid(gettid());else {self ->set_cached_pid(parent_pid);return result;
fork进程结束后会在ForkAndSpecializeCommon函数中调用CallStaticVoidMethod。这就是反射调用zygote.callPostForkChildHooks()
3.4.9 zygote.callPostForkChildHooks() 1 2 3 4 private static void callPostForkChildHooks (int debugFlags, boolean isSystemServer, String instructionSet) postForkChild (debugFlags, isSystemServer, instructionSet);
3.4.10 ZygoteHooks.postForkChild() 源码位于libcore/dalvik/src/main/java/dalvik/system/ZygoteHooks.java
1 2 3 4 5 public void postForkChild(int debugFlags , String instructionSet ) {PostForkChild(token , debugFlags , instructionSet ) ;Math .RandomSeedInternal(System.currentTimeMillis () );
nativePostForkChild又通过jni调用dalvik_system_ZygoteHooks.ZygoteHooks_nativePostForkChild方法
3.4.11 dalvik_system_ZygoteHooks.ZygoteHooks_nativePostForkChild() 源码位于art/runtime/native/dalvik_system_ZygoteHooks.cc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 static void ZygoteHooks_nativePostForkChild (JNIEnv* env, jclass, jlong token, jint debug_flags, jboolean is_system_server, jstring instruction_set) reinterpret_cast <Thread*>(token);InitAfterFork ();EnableDebugFeatures (debug_flags);if (Trace::GetMethodTracingMode () != TracingMode::kTracingInactive) {GetOutputMode ();GetMode ();size_t buffer_size = Trace::GetBufferSize ();Abort ();if (output_mode == Trace::TraceOutputMode::kStreaming) {const char * proc_name_cutils = get_process_name ();if (proc_name_cutils != nullptr ) {if (proc_name_cutils == nullptr || proc_name == "zygote" || proc_name == "zygote64" ) {pid_t pid = getpid ();StringPrintf ("%u" , static_cast <uint32_t >(pid));StringPrintf ("/data/misc/trace/%s.trace.bin" , proc_name.c_str ());Start (trace_file.c_str (),-1 ,0 , 0 ); if (thread->IsExceptionPending ()) {ScopedObjectAccess soa (env) ;ClearException ();if (instruction_set != nullptr && !is_system_server) {ScopedUtfChars isa_string (env, instruction_set) ;GetInstructionSetFromString (isa_string.c_str ());if (isa != kNone && isa != kRuntimeISA) {Current ()->InitNonZygoteOrPostFork (c_str ());else {Current ()->InitNonZygoteOrPostFork (nullptr );
3.4.12 Runtime::InitNonZygoteOrPostFork() 源码位于art/runtime/runtime.cc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 void Runtime::InitNonZygoteOrPostFork(bool is_system_server, NativeBridgeAction action, const char* isa) {false ;if (is_native_bridge_loaded_) {switch (action) {case NativeBridgeAction::kUnload:false ;break ;case NativeBridgeAction::kInitialize:break ;if (!is_system_server &&
fork完成后继续Zygote.forkAndSpecialize方法第三步
3.4.12 ZygoteHooks.postForkCommon() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public void postForkCommon() {Daemons .() ;() {ReferenceQueueDaemon .INSTANCE .() ;FinalizerDaemon .INSTANCE .() ;FinalizerWatchdogDaemon .INSTANCE .() ;HeapTaskDaemon .INSTANCE .() ;
主要作用是在fork新进程后将之前停掉的四个Daemon线程启动起来
forkAndSpecialize 总结
preFork:停止4个Daemon子线程,初始化GC
nativeForkAndSpecialize:调用Linux的fork()子进程,设置新进程的主线程id,重置gc性能数据,设置信号处理函数等功能
postForkCommon:重新启动四个daemon子线程
forkAndSpecialize执行结束,即创建新进程后,会有两次返回,第一次回到ZygoteConnection.runOnce方法,执行子进程handleChildProc方法;第二次回到该方法,执行zygote进程的handleParentProc方法
3.4.13 回调子进程ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 private void handleChildProc(Arguments parsedArgs,new Stderr )if (descriptors != null ) {try {0 ], STDIN_FILENO);1 ], STDOUT_FILENO);2 ], STDERR_FILENO);for (FileDescriptor fd: descriptors ) {new Stderr = System.err;catch (ErrnoException ex) {"Error reopening stdio" , ex);if (parsedArgs.niceName != null ) {if (parsedArgs.invokeWith != null ) {else {null );
3.4.14 RuntimeInit.zygoteInit() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 public static final void zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion , String[] argv , ClassLoader classLoader ) Trace .Begin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "RuntimeInit" ) ;LogStreams() ; Init() ; ZygoteInit() ; Init(targetSdkVersion , argv , classLoader ) ;
3.4.15 RuntimeInit.commonInit() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 private static final void commonInit() {Thread .DefaultUncaughtExceptionHandler(new UncaughtHandler() );TimezoneGetter .Instance(new TimezoneGetter() {Id() {SystemProperties ."persist.sys.timezone" );TimeZone .Default(null ) ;LogManager .LogManager() .reset() ;new AndroidConfig() ;DefaultUserAgent() ;System .Property("http.agent" , userAgent ) ;NetworkManagementSocketTagger .() ;
3.4.16 RuntimeInit.nativeZygoteInit() nativeZygoteInit()所对应的jni方法如下,源码位于frameworks/base/core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 static void com_android_internal_os_RuntimeInit_nativeZygoteInit(JNIEnv* env , jobject clazz ) ZygoteInit() ;
3.4.17 app_main.onZygoteInit() 源码位于 frameworks/base/cmds/app_process/app_main.cpp
1 2 3 4 5 virtual void onZygoteInit()proc = ProcessState::self ();proc ->startThreadPool(); // 启动新binder线程
ProcessState::self():主要工作是调用open()打开/dev/binder驱动设备,再利用mmap()映射内核的地址空间,将Binder驱动的fd赋值ProcessState对象中的变量mDriverFD,用于交互操作。startThreadPool()是创建一个新的binder线程,不断进行talkWithDriver(),与Binder驱动交流
继续执行zygoteInit方法中的最后一个方法
3.4.18 RuntimeInit.applicationInit() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 private static void applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion , String[] argv , ClassLoader classLoader ) SetExitWithoutCleanup(true ) ;VMRuntime .Runtime() .setTargetHeapUtilization(0.75f) ;VMRuntime .Runtime() .setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion ) ;try {new Arguments(argv ) ; Trace .End(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER) ;StaticMain(args .startClass , args .startArgs , classLoader ) ;
3.4.19 RuntimeInit.invokeStaticMain() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 private static void invokeStaticMain(String className , String[] argv , ClassLoader classLoader ) Class .for Name(className , true , classLoader ) ; ... Method m;try {Method("main" , new Class[] { String[].class }) ; ... } catch (SecurityException ex) { ... }new ZygoteInit.MethodAndArgsCaller(m , argv ) ;
重点看最后一个方法,通过反射获取ActivityThread类的main方法参数,然后抛出MethodAndArgsCaller异常,其中构造方法中m是指main方法,argv是AMS发送过来的参数列表;但是抛出异常后怎么弄呢,我们知道一个方法抛异常,会一直往上走到调用方法,直到一个方法捕获了异常。在这里就会一直抛到ZygoteInit.main方法才捕获了异常,然后去执行MethodAndArgsCaller.run方法
3.4.20 MethodAndArgsCaller.run() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 public static class MethodAndArgsCaller extends Exception implements Runnable {private final Method mMethod;private final String [] mArgs;public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String [] args) {public void run() {try {null , new Object [] { mArgs });catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {throw new RuntimeException (ex);catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {Throwable cause = ex.getCause();if (cause instanceof RuntimeException ) {throw (RuntimeException ) cause;else if (cause instanceof Error ) {throw (Error ) cause;throw new RuntimeException (ex);
走到这里就要进入ActivityThread了,它管理着应用程序进程中主线程的执行,在ActivityManager请求时调度和执行Activity,Service,Broadcast和其它操作
3.4.21 ActivityThread.main() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 public static void main (String [] args) prepareMainLooper ();new ActivityThread ();attach (false );if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {getHandler ();loop ();throw new RuntimeException ("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited" );
主要工作:设置进程名,打开binder驱动,启动新的binder线程;然后设置art虚拟机参数,再反射调用目标类的main()方法,即ActivityThread.main()方法
至此,进程创建完毕,并且也有了主线程,剩下的便是启动Activity和关联context等初始化操作了
3.4.22 回调zygote进程ZygoteConnection.handleParentProc() 子进程fork方法执行完成回调第一次给子进程后,还会回调一次给zygote进程
具体是在ZygoteConnection.runOnce中调用handleParentProc
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 private boolean handleParentProc (int pid, FileDescriptor[] descriptors, FileDescriptor pipeFd, Arguments parsedArgs) if (pid > 0 ) {setChildPgid (pid);try {writeInt (pid);writeBoolean (usingWrapper);catch e (TAG, "Error writing to command socket" , ex);return true ;return false ;
这个方法主要是为了通知system server进程,新进程已经创建完成
注意
APP或者桌面启动,需要使用Binder机制告诉AMS(因为启动方有自己的进程,AMS在system server进程),AMS请求zygote进程是通过Socket
Process.start方法是阻塞的,只有等进程创建完成才会返回
zygote进程fork进程一次,会有两次返回,在zygote进程和子进程分别返回一次,这样子线程就能执行ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc及以后的逻辑;zygote进程通过ZygoteConnection.handleParentProc通知system server进程新进程已经创建完成
fork解释 可能你会疑虑,明明是在zygote进程中的ZygoteConnection.runOnce方法中去执行fork操作,那么fork结束后返回不应该还是在zygote进程中吗?
这里需要了解下fork的逻辑:
fork()采用copy on write技术,这是linux创建进程的标准方法,调用一次,返回两次。当父子进程任一方修改内存数据时(这是on-write时机),才发生缺页中断,从而分配新的物理内存(这是copy操作)。
其实就是fork之后,操作系统会复制一个与父进程完全相同的子进程,虽说是父子关系,但是在操作系统看来,他们更像兄弟关系,这2个进程共享代码空间,但是数据空间是互相独立的,子进程数据空间中的内容是父进程的完整拷贝,指令指针也完全相同,子进程拥有父进程当前运行到的位置(两进程的程序计数器pc值相同,也就是说,子进程是从fork返回处开始执行的)
可以这样想象,子进程就是把zygote进程复制了一遍,两个进程都阻塞在这里;但在fork之后,他们就开始分别作不同的工作,正如fork原意【分支】一样,在zygote进程的ZygoteConnection.runOnce方法中,fork返回子进程id,然后执行ZygoteConnection.handleParentProc;但是在子进程的ZygoteConnection.runOnce方法中,fork返回是0,就会去执行ZygoteConnection.handleChildProc;这样父子进程从此分家
4. ActivityThrad的工作逻辑 4.1 前言 我们知道在Sun的Java体系中和C语言中的类或者程序入口点都是main方法,那我们的Android程序入口是不是也是某个类的main方法呢?
有一点很奇怪的是,我们平时开发中好像没接触过main方法,基本上都是与四大组件(还有一个Fragment)和Application打交道;要想弄清楚这是怎么回事,就必须要了解下当你点击手机桌面上某个APP的icon后,它是怎么从无到有运行在你的眼前的呢?
当一个应用进程被创建之后,会把ActivityThread这个类加载到新的进程中来,接下来这个应用的一切操作(比如Activity的创建启动)就从ActivityThread这个类开始展开
4.2 类简称
ActivityManagerService:AMS
ActivityManagerNative:AMN
ActivityManagerProxy:AMP
ActivityThread :AT
ApplicationThread:APT
ApplicationThreadNative:ATN
ApplicationThreadProxy:ATP
ActivityStackSupervisor:ASS
4.3 类简介 这个章节的分析将会接触到大量跨进程通信,需要用到AIDL,其中涉及到的类及Activity启动相关类如下,AIDL的实现模式都是固定的
4.3.1
IActivityManager:作为应用进程请求系统进程的接口,这时候应用进程是客户端进程,系统进程是服务端进程,客户端和服务端进程都实现且遵循这个接口规则
ActivityManagerNative:作为服务端的“桩(Stub)”,其主要职责就是对远程(客户端进程)传递过来的数据进行”反序列化(unparcel)”
ActivityManagerProxy:作为服务的“代理(Proxy)”,运行在客户端进程,其主要职责就是将数据进行“序列化(parcel)”,再传递给远程的“桩(Stub)”
ActivityManagerService:IActivityManager接口中定义的业务的具体实现,运行在服务端,对“桩(Stub)”做了继承扩展
4.3.2
IApplicationThread: 作为系统进程请求应用进程的接口,这时候应用进程是服务端进程,系统进程是客户端进程,客户端和服务端进程都实现且遵循这个接口规则
ApplicationThreadNative:同理于ActivityManagerNative
ApplicationThreadProxy:同理于ActivityManagerProxy
ApplicationThread:同理于ActivityManagerService,负责响应系统进程发起的请求,帮助AMS管理相关Application中的Activity的生命周期,是ActivityThread内部类(ActivityThread是应用进程的主线程),接收到系统进程请求后通过Handler往主线程发消息,这样ApplicationThread就轻松将具体执行任务的工作转交给了主线程,用来实现AMS和AT之间的交互
4.3.3
ProcessRecord:保存了进程运行时的信息,AMS通过ProcessRecord来维护进程运行时的状态信息,需要将应用进程绑定到ProcessRecord才能开始一个Application的构建(每个应用进程在AMS对应一个ProcessRecord)
ActivityRecord:保存Activity运行时的信息,AMS通过ActivityRecord来维护Activity运行时的状态信息,需要将Activity绑定到AMS中的ActivityRecord才能开始Activity的生命周期(每个Activity在AMS对应一个ActivityRecord,其实就是服务器端的Activity对象的映像)
TaskRecord:AMS抽象出来的一个Task的概念,是记录ActivityRecord的栈,一个“Task”包含若干个ActivityRecord。AMS用TaskRecord确保Activity启动和退出的顺序,如果了解过Activity的启动模式就知道这个用处了
ActivityStack:AMS对Activity设计的一种堆栈机制用于管理Activity,为了让这许多Activity协同工作而不至于产生混乱,其遵循先进后出的原则,系统总是显示位于栈顶的Activity
4.3.4
ActivityThread:APP的入口类,从main方法开始执行,就是大家口中的UI线程或者主线程,与AMS一起完成四大组件的工作
Instrumentation:每一个应用程序只有一个Instrumentation实例,在BindApplication创建的,每个Activity内部拥有一个该对象的引用,ActivityThread对组件的操作最后都是交给它去做具体的执行
4.3.5
ApplicationInfo:保存了应用程序的信息,包括AndroidManifest.xml中检索的信息
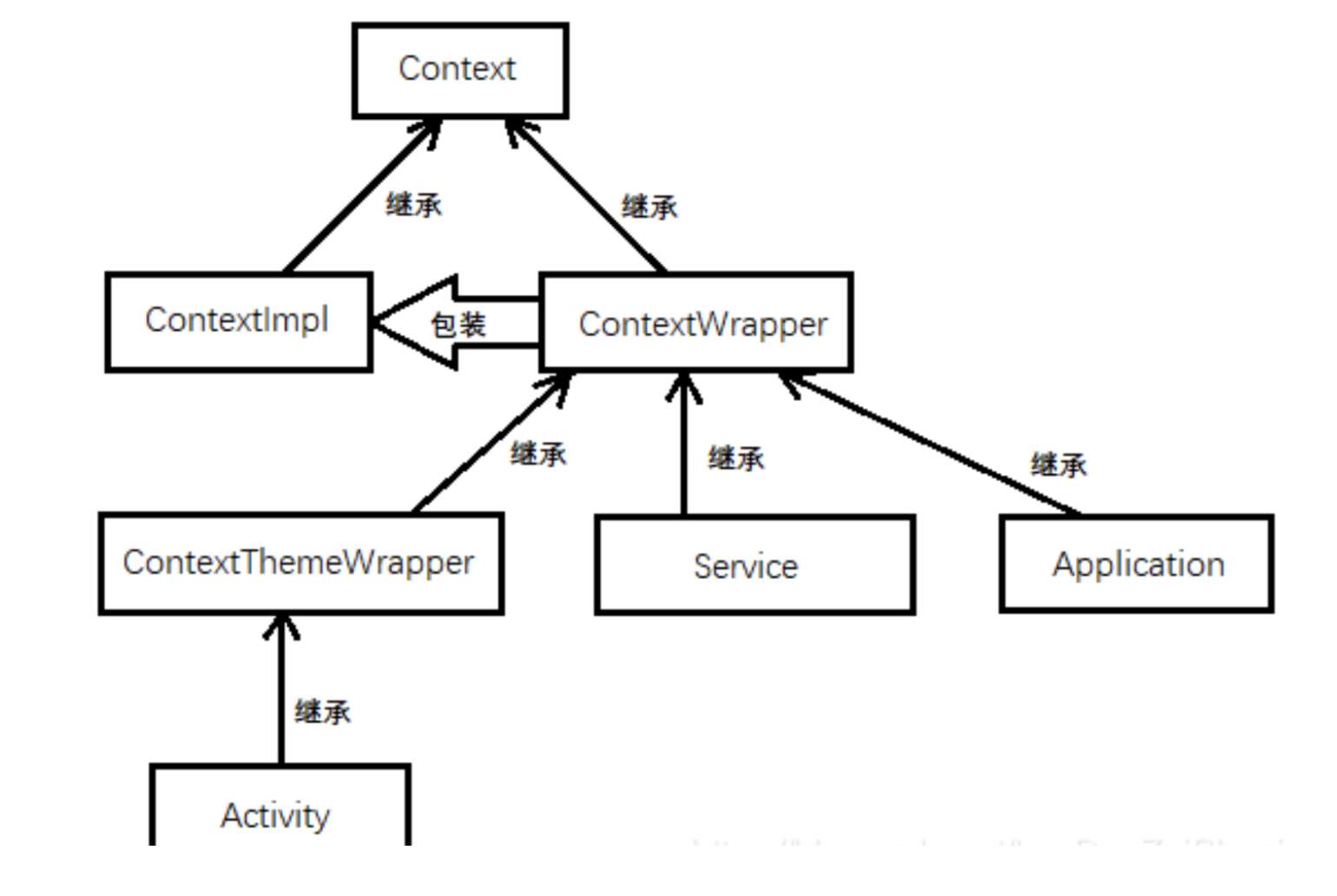
Context:Activity的上下文
ContextWrapper:继承Context,为了使用方便,对Context进行包装,而无需修改Context,内部包含一个真正的Context引用,调用ContextWrapper的方法都会被转向其所包含的真正的Context对象,即ContextImpl对象
Application:继承ContextWrapper,ActivityThread的上下文,用户可以继承它自定义自己的Application类,用于维护全局应用程序状态的基类
ContextImpl:继承Context,真正实现了Context中所有函数,应用程序中调用的各种Context类的方法,其实现均来自于该类;它为Activity和其他应用程序组件提供基本上下文对象
4.3.6 代理和桩的理解 “代理(Proxy)”和“桩(Stub)”是Binder接口实现时成对出现的概念。可以对应到一个生活中的例子:银行的取款机就像是银行的业务代理(Proxy),客户只需要通过取款机,就能方便地完成存、取款等业务。对于客户来说,不用关心银行是什么样,钱到哪去了,只要通过代理能完成自己的业务就行了;对于取款机这个代理而言,它需要连接银行的服务器(Stub),完成数据传递,将客户的操作反馈到中心
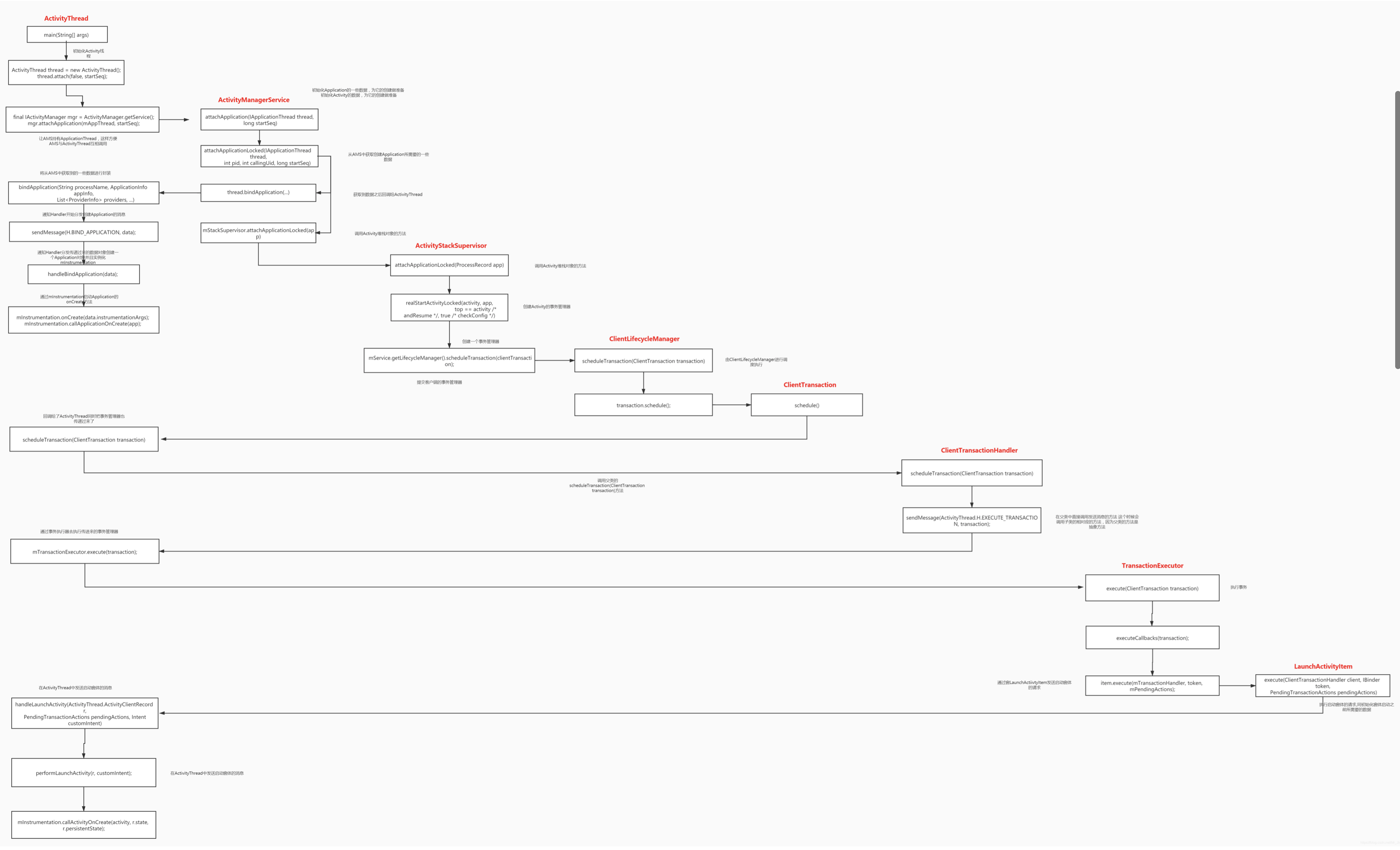
4.4 ActivityThread入口 源码位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityThread.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 public static void main(String[] args) {Environment .ForCurrentUser() ;Environment .UserConfigDirectory(UserHandle.myUserId () );TrustedCertificateStore .DefaultUserDirectory(configDir ) ;Process .ArgV0("<pre-initialized>" ) ;Looper .MainLooper() ;new ActivityThread() ;false );if (sMainThreadHandler == null) {Handler() ;Looper .() ;new RuntimeException("Main thread loop unexpectedly exited" ) ;
这个方法三处比较重要
4.4.1 AT.attach() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 private void attach (boolean systemthis ;if (!system) { new Runnable (@Override public void run ("<pre-initialized>" ,try {catch (RemoteException ex) {throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();new Runnable (@Override public void run (if (!mSomeActivitiesChanged) {return ;if (dalvikUsed > ((3 *dalvikMax)/4 )) {if (DEBUG_MEMORY_TRIM) Slog.d(TAG, "Dalvik max=" + (dalvikMax/1024 )" total=" + (runtime.totalMemory()/1024 )" used=" + (dalvikUsed/1024 ));false ;try {catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();else {"system_process" ,try {new Instrumentation();this , getSystemContext().mPackageInfo);true , null );catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate Application():" + e.toString(), e);new DropBoxReporter());new ComponentCallbacks2 (@Override public void onConfigurationChanged (Configuration newConfig )if (mResourcesManager.applyConfigurationToResourcesLocked(newConfig, null )) {if (mPendingConfiguration == null ||@Override public void onLowMemory (@Override public void onTrimMemory (int level )
该方法的参数表明是否是system app调用,然后赋值mSystemThread;显然这里是普通app,进入第一个分支
接下来调用ensureJitEnabled()方法,目的是开启虚拟机即时编译功能,Jit全称Just-In-Time,JIT 是一种在运行时同步将字节码转化成机器码的编译器,Dalvik 直接运行转化后的机器码
通过ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()获取AMS的Binder代理对象,然后将APT对象发送给AMS,因为APT继承ATN,这样间接继承了IBinder接口,具备跨进程传输能力
通过BinderInternal类去观察虚拟机内存使用情况
添加dropbox日志到libcore
添加Config回调接口
接下来从ActivityManagerNative.getDefault()开始分析
4.4.2 AMN.getDefault() 源码位于frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/ActivityManagerNative.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 static public IActivityManager getDefault (return gDefault.get ();private static final Singleton <IActivityManager > gDefaultnew Singleton<IActivityManager>() {protected IActivityManager create ("activity" );if (false ) {"ActivityManager" , "default service binder = " + b);if (false ) {"ActivityManager" , "default service = " + am);return am;static public IActivityManager asInterface (IBinder obj )if (obj == null ) {return null ;in =if (in != null ) {return in ;return new ActivityManagerProxy(obj);
当前应用所在进程与AMS所在的system server进程不是一个进程,如果想要与AMS通信,就必须要使用Binder机制,这里跨进程通信的过程就是一个典型的AIDL实现
这里是把ActivityThread当做Client,AMS当做Server,这里是跨进程,就需要获取AMS在Client的Binder代理对象,即构建AMP返回,所以这里的IActivityManager实质上是AMP对象,接下来进入AMP
4.4.3 AMP.attachApplication() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 public void attachApplication(IApplicationThread app ) throws RemoteExceptionParcel .() ;Parcel .() ;InterfaceToken(IActivityManager.descriptor ) ;StrongBinder(app .asBinder () );0 );Exception() ;() ;() ;
因为是Binder代理对象,所以这里的mRemote是BinderProxy类型,进入看看
4.4.4 BinderProxy.transact() 源码位于 frameworks/base/core/java/android/os/Binder.java
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 public boolean transact (int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException this , code, data, "Unreasonably large binder buffer" );if (Binder.isTracingEnabled()) { Binder.getTransactionTracker().addTrace(); }return transactNative (code, data, reply, flags) public native boolean transactNative(int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply,int flags) throws RemoteException
这里最终调用到了native层,接下来经过一系列函数调用,最终调用到了**talkWithDriver()*跟驱动交互,这个函数最后通过ioctl系统调用,Client进程陷入内核态,Client调用attachApplication方法的线程挂起等待返回;驱动完成一系列的操作之后唤醒AMS所在进程,调用了AMS所在进程本地对象的onTransact函数(实际上由Server端线程池完成),这里就调用了AMN的onTransact方法(AMN即Binder本地对象)
4.4.5 AMN.onTransact() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 public boolean onTransact (int code, Parcel data, Parcel reply, int flags) throws RemoteException {switch (code) {case ATTACH_APPLICATION_TRANSACTION: {if (app != null ) {return true ;return super .onTransact (code, data, reply, flags)
在AMS所在进程里面,onTransact根据编号调用相关函数;在这个例子里面,由AMS的Binder本地对象(AMN)调用了Server端的attachApplication方法,从这里开始就正式进入AMS了
这边很重要的一点是:
4.4.6 AMS.attachApplication() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 @OverrideApplication(IApplicationThread thread ) {int callingPid = Binder .CallingPid() ;Binder .CallingIdentity() ;ApplicationLocked(thread , callingPid ) ;Binder .CallingIdentity(origId ) ;
这里的thread就是ATP了,AMS就用这个跟APP进程的APT通信
4.4.7 AMS.attachApplicationLocked() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 private final boolean attachApplicationLocked(IApplicationThread thread,int pid) {if (pid != MY_PID && pid >= 0 ) {else {null ;if (app == null ) {if (pid > 0 && pid != MY_PID) {else {try {catch (Exception e) {return false ;if (app.thread != null ) {true , true );final String processName = app.processName;try {new AppDeathRecipient(0 );catch (RemoteException e) {"link fail" , processName);return false ;null ;false , false );false ;false ;false ;false ;boolean normalMode = mProcessesReady || isAllowedWhileBooting(app.info);List <ProviderInfo> providers = normalMode ? generateApplicationProvidersLocked(app) : null ;if (providers != null && checkAppInLaunchingProvidersLocked(app)) {try {null if (profileFd != null ) {null ? null new ProfilerInfo(profileFile, profileFd, samplingInterval, profileAutoStop);new Configuration(mConfiguration), app.compat,false , null );catch (Exception e) {"bind fail" , processName);return false ;boolean badApp = false ;boolean didSomething = false ;if (normalMode) {try {if (mStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked(app)) {true ;catch (Exception e) {true ;if (!badApp) {try {catch (Exception e) {true ;if (!badApp && isPendingBroadcastProcessLocked(pid)) {try {catch (Exception e) {true ;if (!badApp && mBackupTarget != null && mBackupTarget.appInfo.uid == app.uid) {try {catch (Exception e) {true ;if (badApp) {"error during init" , true );false , true );return false ;if (!didSomething) {return true ;
小结
通过pid查找当前进程对应的ProcessRecord
如果ProcessRecord == null,说明正在attach的进程不存在,如果pid有效就杀掉pid对应的进程;反之让刚创建的activitythread退出looper循环;最后直接return
如果查找出来的ProcessRecord 中保存的IApplicationThread不为空,说明它是上个进程的,那就需要清除它
注册该进程的死亡回调,当进程死亡时会通过binder回调,来通知system_server进程死亡的消息
重新设置ProcessRecord信息
调用thread.bindApplication绑定Application到ActivityThread
处理activity,service,Broadcast receiver
kill掉bad应用
我们先看第二步,退出looper循环
thread.scheduleExit()
这里的thread是入参IApplicationThread,由上面分析可知,传过来的是APT在客户端的代理ATP,那就走到ATP.scheduleExit
4.4.8 ATP.scheduleExit() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 public final void scheduleExit() throws RemoteException {Parcel data = Parcel .obtain();data .writeInterfaceToken(IApplicationThread .descriptor );SCHEDULE_EXIT_TRANSACTION , data , null,IBinder .FLAG_ONEWAY );data .recycle();
因为是代理对象,所以这里的mRemote是BinderProxy类型,调用后经过底层Binder调用会走到服务端的ATN.onTransact
4.4.9 ATN.onTransact() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 public boolean onTransact(int code , Parcel data , Parcel reply , int flags ) Interface(IApplicationThread.descriptor ) ;Exit() ;true ;Transact(code , data , reply , flags ) ;
scheduleExit()具体实现在APT
4.4.10 APT.scheduleExit() 1 2 3 public final void scheduleExit () null );
继续调用到AT
4.4.11 AT.sendMessage() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 private void sendMessage(int what , Object obj ) {Message(what , obj , 0, 0, false ) ;private void sendMessage(int what , Object obj , int arg1 , int arg2 , boolean async ) {if (DEBUG_MESSAGES) Slog ."SCHEDULE " + what + " " + mH.codeToString(what ) ": " + arg1 + " / " + obj);Message .() ;if (async) {Asynchronous(true ) ;Message(msg ) ;private class H extends Handler {Message(Message msg ) {if (mInitialApplication != null) {Terminate() ;Looper .Looper() .quit() ;
最终会将主线程的消息队列清空并退出looper;这一系列调用就是一个AIDL的实现
再看第四步,注册APP进程的死亡通知
thread.asBinder().linkToDeath
上面说了thread是代理对象,调用的是ATP.asBinder(),通过adBinder获取到的Binder类型是BinderProxy
4.4.12 BinderProxy.linkToDeath() 1 2 public native void linkToDeath (DeathRecipient recipient, int flags) throws RemoteException ;
这是一个native方法,经过jni调用后
4.4.13 android_util_Binder.linkToDeath() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 static const JNINativeMethod gBinderProxyMethods[] = {"linkToDeath" , "(Landroid/os/IBinder$DeathRecipient;I)V" , (void *)android_os_BinderProxy_linkToDeath}static void android_os_BinderProxy_linkToDeath (JNIEnv* env, jobject obj, jobject recipient, jint flags) if (recipient == NULL ) {jniThrowNullPointerException (env, NULL );return ;getBPNativeData (env, obj);get ();LOGDEATH ("linkToDeath: binder=%p recipient=%p\n" , target, recipient);if (!target->localBinder ()) {get ();new JavaDeathRecipient (env, recipient, list);status_t err = target->linkToDeath (jdr, NULL , flags);if (err != NO_ERROR) {clearReference ();signalExceptionForError (env, obj, err, true );status_t BpBinder::linkToDeath ( const sp<DeathRecipient>& recipient, void * cookie, uint32_t flags) if (!mObitsSent) { if (!mObituaries) {new Vector<Obituary>;if (!mObituaries) {return NO_MEMORY;getWeakRefs ()->incWeak (this );self ();requestDeathNotification (mHandle, this );flushCommands ();ssize_t res = mObituaries->add (ob);return res >= (ssize_t )NO_ERROR ? (status_t )NO_ERROR : res;return DEAD_OBJECT;status_t IPCThreadState::requestDeathNotification (int32_t handle, BpBinder* proxy) writeInt32 (BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION);writeInt32 ((int32_t )handle);writePointer ((uintptr_t )proxy);return NO_ERROR;void IPCThreadState::flushCommands () if (mProcess->mDriverFD <= 0 )return ;talkWithDriver (false );
这里最终会调用talkWithDriver告诉Binder驱动
4.4.14 IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 status_t IPCThreadState::talkWithDriver (bool doReceive) if (mProcess->mDriverFD <= 0 ) {return -EBADF;const bool needRead = mIn.dataPosition () >= mIn.dataSize ();const size_t outAvail = (!doReceive || needRead) ? mOut.dataSize () : 0 ;uintptr_t )mOut.data ();if (doReceive && needRead) {dataCapacity ();uintptr_t )mIn.data ();else {0 ;0 ;0 ;0 ;status_t err;do {if (ioctl (mProcess->mDriverFD, BINDER_WRITE_READ, &bwr) >= 0 )else if (mProcess->mDriverFD <= 0 ) {while (err == -EINTR);return err;static long binder_ioctl (struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg) int ret;struct binder_proc *proc =struct binder_thread *thread ;wait_event_interruptible (binder_user_error_wait, binder_stop_on_user_error < 2 );binder_lock (__func__);binder_get_thread (proc); switch case BINDER_WRITE_READ: binder_ioctl_write_read (filp, cmd, arg, thread); if (ret)goto err;break ;case ...0 ;if (thread)binder_unlock (__func__);return ret;static int binder_ioctl_write_read (struct file *filp, unsigned int cmd, unsigned long arg, struct binder_thread *thread) int ret = 0 ;struct binder_proc *proc =void __user *ubuf = (void __user *)arg;struct binder_write_read bwr ;if (copy_from_user (&bwr, ubuf, sizeof goto out;if (bwr.write_size > 0 ) { binder_thread_write (proc, thread,if (bwr.read_size > 0 ) { if (copy_to_user (ubuf, &bwr, sizeof goto out;return ret;static int binder_thread_write (struct binder_proc *proc, struct binder_thread *thread, binder_uintptr_t binder_buffer, size_t size, binder_size_t *consumed) uint32_t cmd;void __user *buffer = (void __user *)(uintptr_t )binder_buffer;void __user *ptr = buffer + *consumed;void __user *end = buffer + size;while (ptr < end && thread->return_error == BR_OK) {get_user (cmd, (uint32_t __user *)ptr); switch case BC_REQUEST_DEATH_NOTIFICATION:list_add_tail (&ref->death->work.entry, &thread->todo);break ;case ...;
最后一步表明只要对端进程挂掉,Binder是在底层可以从todo链表中拿出来client的信息,然后调用对应的回调方法
接下来看第六步,绑定应用
thread.bindApplication
调用原理跟上面一样,这里就不在继续阐述了,最终会调用到APT.bindApplication
4.4.15 APT.bindApplication() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 public final void bindApplication(String processName, ApplicationInfo appInfo,List <ProviderInfo > providers, ComponentName instrumentationName,ProfilerInfo profilerInfo, Bundle instrumentationArgs,IInstrumentationWatcher instrumentationWatcher,IUiAutomationConnection instrumentationUiConnection, int debugMode,Configuration config,CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, Map <String , IBinder > services, Bundle coreSettings) {if (services != null) {Setup the service cache in the ServiceManager ServiceManager .initServiceCache(services);AppBindData data = new AppBindData ();data .processName = processName;data .appInfo = appInfo;data .providers = providers;data .instrumentationName = instrumentationName;data .instrumentationArgs = instrumentationArgs;data .instrumentationWatcher = instrumentationWatcher;data .instrumentationUiAutomationConnection = instrumentationUiConnection;data .debugMode = debugMode;data .enableBinderTracking = enableBinderTracking;data .trackAllocation = trackAllocation;data .restrictedBackupMode = isRestrictedBackupMode;data .persistent = persistent;data .config = config;data .compatInfo = compatInfo;data .initProfilerInfo = profilerInfo;H .BIND_APPLICATION , data );Bundle coreSettings) {H .SET_CORE_SETTINGS , coreSettings);
这里通过handler向主线程(AT)发送了两条消息SET_CORE_SETTINGS,BIND_APPLICATION
4.4.16 AT.H.SET_CORE_SETTINGS、AT.H.BIND_APPLICATION 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private class H extends Handler {Message(Message msg ) {Trace .Begin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "setCoreSettings" ) ;SetCoreSettings((Bundle) msg.obj);Trace .End(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER) ;Trace .Begin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "bindApplication" ) ;BindApplication(data ) ;Trace .End(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER) ;
4.4.17 AT.handleSetCoreSettings() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 private void handleSetCoreSettings(Bundle coreSettings ) {CoreSettingsChange() ;private void onCoreSettingsChange() {Int(Settings.Global.DEBUG_VIEW_ATTRIBUTES, 0) != 0 ;if (debugViewAttributes != View .View .for (Map.Entry<IBinder, ActivityClientRecord> entry : mActivities.entrySet() ) {RelaunchActivity(entry .getKey () , null, null, 0 , false , null, null, false ,false );
4.4.18 AT.handleBindApplication() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 private void handleBindApplication(AppBindData data ) {if (data .trackAllocation) {true );data ;data .config);data .config);if (data .initProfilerInfo != null ) {data .initProfilerInfo.profileFile;data .initProfilerInfo.profileFd;data .initProfilerInfo.samplingInterval;data .initProfilerInfo.autoStopProfiler;data .processName);data .processName,if (data .persistent) {if (!ActivityManager.isHighEndGfx()) {false );if (mProfiler.profileFd != null ) {if (data .appInfo.targetSdkVersion <= android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB_MR1) {data .appInfo.targetSdkVersion);null );data .config.getLocales());data .config, data .compatInfo);data .config.densityDpi;data .info = getPackageInfoNoCheck(data .appInfo, data .compatInfo);if (data .appInfo.targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.HONEYCOMB) {if (data .appInfo.targetSdkVersion >= Build.VERSION_CODES.N) {"Setup proxies" );final IBinder b = ServiceManager.getService(Context.CONNECTIVITY_SERVICE);if (b != null ) {final IConnectivityManager service = IConnectivityManager.Stub.asInterface(b);try {final ProxyInfo proxyInfo = service.getProxyForNetwork(null );catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();final InstrumentationInfo ii;if (data .instrumentationName != null ) {try {null , getPackageManager())data .instrumentationName, 0 );catch (PackageManager.NameNotFoundException e) {throw new RuntimeException("Unable to find instrumentation info for: " + data .instrumentationName);data .appInfo, ii);data .info.getAppDir();data .info.getSplitAppDirs();data .info.getLibDir();else {null ;final ContextImpl appContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this , data .info);if (!Process.isIsolated() && !"android" .equals(appContext.getPackageName())) {final File cacheDir = appContext.getCacheDir();if (cacheDir != null ) {"java.io.tmpdir" , cacheDir.getAbsolutePath());final Context deviceContext = appContext.createDeviceProtectedStorageContext();final File codeCacheDir = deviceContext.getCodeCacheDir();if (codeCacheDir != null ) {data .info, codeCacheDir);if (ii != null ) {final ApplicationInfo instrApp = new ApplicationInfo();final LoadedApk pi = getPackageInfo(instrApp, data .compatInfo,false , true , false );final ContextImpl instrContext = ContextImpl.createAppContext(this , pi);try {final ClassLoader cl = instrContext.getClassLoader();data .instrumentationName.getClassName()).newInstance();catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate instrumentation " data .instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e);final ComponentName component = new ComponentName(ii.packageName, ii.name);init (this , instrContext, appContext, component,data .instrumentationWatcher, data .instrumentationUiAutomationConnection);if (mProfiler.profileFile != null && !ii.handleProfilingnull ) {true ;final File file = new File(mProfiler.profileFile);8 * 1024 * 1024 );else {if ((data .appInfo.flags&ApplicationInfo.FLAG_LARGE_HEAP) != 0 ) {else {final StrictMode.ThreadPolicy savedPolicy = StrictMode.allowThreadDiskWrites();try {data .info.makeApplication(data .restrictedBackupMode, null );if (!data .restrictedBackupMode) {if (!ArrayUtils.isEmpty(data .providers)) {data .providers);10 *1000 );try {data .instrumentationArgs);catch (Exception e) {throw new RuntimeException("Exception thrown in onCreate() of " data .instrumentationName + ": " + e.toString(), e);try {catch (Exception e) {if (!mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {throw new RuntimeException("Unable to create application " + app.getClass().getName()": " + e.toString(), e);finally {
这个方法很长,工作内容如下:
对进程基本参数的设置,比如进程名,时区,资源及兼容性设置;同时添加了对开发者的限制,如不能在主线程使用网络
通过getPackageInfoNoCheck获取LoadedApk对象
实例化ContextImpl,Instrumentation等对象
通过LoadedApk.makeApplication创建应用Application对象
调用Instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate
4.4.19 AT.getPackageInfoNoCheck() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 public final LoadedApk getPackageInfoNoCheck (ApplicationInfo ai, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo) return getPackageInfo (ai, compatInfo, null , false , true , false ) private LoadedApk getPackageInfo (ApplicationInfo aInfo, CompatibilityInfo compatInfo, ClassLoader baseLoader, boolean securityViolation, boolean includeCode, boolean registerPackage) final boolean differentUser = (UserHandle.myUserId() != UserHandle.getUserId(aInfo.uid));synchronized (mResourcesManager) {if (differentUser) {null ;else if (includeCode) else {null ? ref.get() : null ;if (packageInfo == null || (packageInfo.mResources != null new LoadedApk(this , aInfo, compatInfo, baseLoader,0 , registerPackage);if (mSystemThread && "android" .equals(aInfo.packageName)) {if (differentUser) {else if (includeCode) new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo));else {new WeakReference<LoadedApk>(packageInfo));return packageInfo;
这里返回一个LoadedApk对象,这个对象有什么作用呢?
注意:LoadedApk对象是APK文件在内存中的表示,包含apk文件的相关信息,比如应用代码,资源文件,app里的activity和service等都可以从这获取,在使用类加载器的时候需要用到这个对象
4.4.20 LoadedApk.makeApplication() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 public Application makeApplication(boolean forceDefaultAppClass,if (mApplication != null ) {return mApplication;null ;String appClass = mApplicationInfo.className;if (forceDefaultAppClass || (appClass == null )) {"android.app.Application" ;try {if (!mPackageName.equals("android" )) {this );catch (Exception e) {if (!mActivityThread.mInstrumentation.onException(app, e)) {throw new RuntimeException("Unable to instantiate application " + appClass": " + e.toString(), e);add (app);String > packageIdentifiers = getAssets(mActivityThread)final int N = packageIdentifiers.size ();for (int i = 0 ; i < N; i++) {final int id = packageIdentifiers.keyAt(i);if (id == 0x01 || id == 0x7f ) {continue ;return app;
4.4.21 Instrumentation.newApplication() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 public Application new Application(ClassLoader cl , String className , Context context ) new Application(cl .loadClass (className ) , context);new Application(Class<?> clazz , Context context ) new Instance() ;
这里通过反射实例化Application ,然后调用attach
4.4.22 Application.attach() 1 2 3 4 5 final void attach(Context context) {BaseContext(context ) ;ContextImpl .Impl(context ) .mPackageInfo;
4.4.23 ContextWrapper.attachBaseContext() 1 2 3 4 5 6 protected void attachBaseContext (Context base )if (mBase != null ) {throw new IllegalStateException("Base context already set" );base ;
这里对mBase 进行赋值,实际类型是ContextImpl
4.4.24 Instrumentation.callApplicationOnCreate() 1 2 3 public void callApplicationOnCreate (Application app )
4.4.25 Application.onCreate() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 @CallSuper public void onCreate (
这里就会回调Application的onCreate方法,我们通常会继承这个类,重写这个方法,做一些APP的初始化操作,但是切记不要做耗时复杂操作,因为这里应用才刚创建,还在初始化,可能会导致应用启动黑屏一段时间的情况
AMS.attachApplicationLocked方法执行完bindApplication后,对照着顶部目录看,接下来就是该方法第七步,启动Activity等操作了
4.4.26 ActivityStackSupervisor.attachApplicationLocked() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 boolean attachApplicationLocked (ProcessRecord app) throws RemoteException final String processName = app.processName;boolean didSomething = false ;for (int displayNdx = mActivityDisplays.size () - 1 ; displayNdx >= 0 ; --displayNdx) {valueAt (displayNdx).mStacks;for (int stackNdx = stacks.size () - 1 ; stackNdx >= 0 ; --stackNdx) {final ActivityStack stack = stacks.get (stackNdx);if (!isFocusedStack (stack)) {continue ;topRunningActivityLocked ();if (hr != null) {if (hr.app == null && app.uid == hr.info.applicationInfo.uidequals (hr.processName)) {try {if (realStartActivityLocked (hr, app, true , true )) {true ;catch throw e;if (!didSomething) {ensureActivitiesVisibleLocked (null, 0 , !PRESERVE_WINDOWS);return didSomething;
接下来就要真正启动activity了,到这里也快接近尾声了
4.4.27 ActivityStackSupervisor.realStartActivityLocked() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 final boolean realStartActivityLocked(ActivityRecord r, ProcessRecord app,boolean andResume, boolean checkConfig) throws RemoteException {if (!allPausedActivitiesComplete()) {return false ;if (andResume) {0 );true );if (checkConfig) {null );false );... ... stack = task.stack ;... ... thread .scheduleLaunchActivity(new Intent(r.intent), r.appToken,new Configuration(mService.mConfiguration),new Configuration(task.mOverrideConfig), r.compat, r.launchedFromPackage,if ((app.info.privateFlags&ApplicationInfo.PRIVATE_FLAG_CANT_SAVE_STATE) != 0 ) {if (app.processName.equals (app.info.packageName)) {if (mService.mHeavyWeightProcess != null TAG , "Starting new heavy weight process " + app" when already running " if (r.launchFailed) {stack .requestFinishActivityLocked(r.appToken, Activity.RESULT_CANCELED, null ,"2nd-crash" , false );return false ;false ;if (stack .updateLRUListLocked(r)) {... ... if (r.app != null ) {return true ;
这个方法里这最重要的一步就是app.thread.scheduleLaunchActivity,这里又是一个AIDL实现,app.thread的实际类型是客户端进程在AMS端进程的代理,即ATP;接下来具体过程跟上面分析thread.scheduleExit()的时候一样,这里就不在具体阐述了,直接到ActivityThread
4.4.28 AT.handleLaunchActivity() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 private class H extends Handler Message msg) {case LAUNCH_ACTIVITY : {final ActivityClientRecord r = (ActivityClientRecord ) msg.obj;null , "LAUNCH_ACTIVITY" );break ;private void handleLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent, String reason) {true ;if (r.profilerInfo != null ) {null , null );WindowManagerGlobal .initialize();Activity a = performLaunchActivity(r, customIntent);if (a != null ) {new Configuration (mConfiguration);Bundle oldState = r.state;false , r.isForward,else {try {ActivityManagerNative .getDefault()Activity .RESULT_CANCELED , null ,Activity .DONT_FINISH_TASK_WITH_ACTIVITY );catch (RemoteException ex) {throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
这里调用了两个关键方法
performLaunchActivity
handleResumeActivity
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 private Activity performLaunchActivity(ActivityClientRecord r, Intent customIntent) {if (r.packageInfo == null ) {if (component == null ) {if (r.activityInfo.targetActivity != null ) {new ComponentName (r.activityInfo.packageName,null ;try {new Activity (if (r.state != null ) {catch (Exception e) {if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {throw new RuntimeException ("Unable to instantiate activity " + component": " + e.toString(), e);try {false , mInstrumentation);if (activity != null ) {new Configuration (mCompatConfiguration);if (r.overrideConfig != null ) {null ;if (r.mPendingRemoveWindow != null && r.mPreserveWindow) {null ;null ;this , getInstrumentation(), r.token,if (customIntent != null ) {null ;false ;if (theme != 0 ) {false ;if (r.isPersistable()) {else {if (!activity.mCalled) {throw new SuperNotCalledException ("Activity " + r.intent.getComponent().toShortString() +" did not call through to super.onCreate()" );true ;if (!r.activity.mFinished) {false ;if (!r.activity.mFinished) {if (r.isPersistable()) {if (r.state != null || r.persistentState != null ) {else if (r.state != null ) {true ;catch (SuperNotCalledException e) {throw e;catch (Exception e) {if (!mInstrumentation.onException(activity, e)) {throw new RuntimeException ("Unable to start activity " + component": " + e.toString(), e);return activity;
4.4.30 AT.handleResumeActivity() 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 final void handleResumeActivity(IBinder token,int seq, String reason) {get (token);if (r != null ) {final Activity a = r.activity;final int forwardBit = isForward ?0 ;if (!willBeVisible) {try {catch (RemoteException e) {throw e.rethrowFromSystemServer();if (r.window == null && !a.mFinished && willBeVisible) {window = r.activity.getWindow();window .getDecorView();window .getAttributes();if (r.mPreserveWindow) {true ;false ;if (impl != null ) {if (a.mVisibleFromClient && !a.mWindowAdded) {true ;else if (!willBeVisible) {true ;false );if (!r.activity.mFinished && willBeVisiblenull && !r.hideForNow) {if (r.newConfig != null ) {null ;window .getAttributes();if ((l.softInputModeif (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {window .getDecorView();true ;if (r.activity.mVisibleFromClient) {if (reallyResume) {try {catch (RemoteException ex) {throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();else {try {null ,catch (RemoteException ex) {throw ex.rethrowFromSystemServer();
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 public final ActivityClientRecord performResumeActivity(IBinder token,boolean clearHide, String reason) {if (r != null && !r.activity.mFinished) {if (clearHide) {false ;false ;try {if (r.pendingIntents != null ) {null ;if (r.pendingResults != null ) {null ;false ;false ;null ;null ;catch (Exception e) {if (!mInstrumentation.onException(r.activity, e)) {throw new RuntimeException ("Unable to resume activity " ": " + e.toString(), e);return r;
到这里一个Activity就从无到有被启动且可见了
4.5 流程图 参考文档 从源码解析Android中Zygote进程是如何fork一个APP进程的
Android 10.0系统启动之init进程-[Android取经之路]
从源码解析-Android系统启动流程概述 init进程zygote进程SystemServer进程启动流程
Android zygote 进程的启动过程分析
APP启动流程解析
ActivityThrad的工作逻辑